Table 1.
Comparison of influenza virus and coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2). ↓ means decreas and ↑ means increase.
| Features | Influenza A Virus | SARS-CoV-2 |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
| Year and pandemic name | 1918 (H1N1), 1957 (H2N2), 1968 (H3N2), 2009 (H1N1), and Flu pandemics | 2019 and COVID-19 |
| Virus family | Orthomyxoviridae | Coronaviridae (genus β-CoVs) |
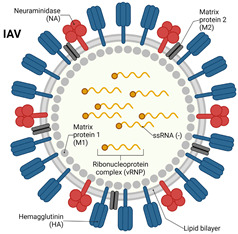
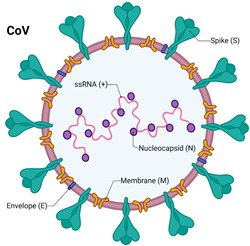
| Structure | An enveloped, negative-sense, and single-stranded RNA virus; slightly ovoid or mostly round; diameter of 80–120 nm | An enveloped, positive-sense, and single-stranded RNA virus; spherical or round in shape; diameter of 60–140 nm |
| Genome size | 13.5 kb | 29.9 kb |
| Mode of transmission | Droplet, aerosol, direct contact, and fecal–oral route | Droplet, aerosol, direct contact, and fecal–oral route |
| Replication sites | Upper respiratory tract and, in severe cases, lower respiratory tract | Starts from the upper respiratory tract, infects the lower respiratory tract, and spreads to other organs (cardiovascular, intestinal, kidney, and nervous system) |
| Incubation period | 1–7 days | 2–14 days (a maximum of 24 days) |
| Host receptor and entry | Terminal glycosides of sialic acid | ACE2 and TMPRSS2 |
| Cellular tropism | Epithelial cells of Respiratory tract: Alveolar Epithelial cells and ciliated cells | Epithelial cells of the respiratory tract: alveolar epithelial cells, ciliated cells, basal cells of the olfactory epithelium, intestinal epithelial cells, renal parenchymal cells, and endothelial cells |
| Viral protein binding to host receptor | HA | Spike (S) protein |
| Replication | Nuclear | Cytoplasm |
| Symptom | Fever, dry cough, sore throat, fatigue, and nasal congestion | High fever, dry cough, fatigue, ARDS, and anosmia |
| Extrapulmonary complications | In rare cases, myocarditis and encephalitis | In most cases, anosmia, thrombosis, stroke, encephalitis, and diarrhea |
| Target for neutralizing antibodies | HA and NA | RBD of the spike protein |
| Hematological parameters | Lymphopenia and CRP ↑ | Type I interferon ↓, neutrophil counts ↑, and significant lymphopenia |
| Variants of concern (VOCs) | 1957 H2N2, 1968 H3N2, and 2009 H1N1 | Alpha, Beta, Gamma, Delta, and Omicron |
| Mortality rate | 0.05–0.1% (seasonal influenza) | ~1–3.4% (higher in early wave) |
| Vaccine availability | Annual seasonal vaccines (inactivated, live) | Multiple vaccines (mRNA, vector-based, inactivated) |
| Mutations/variants | Antigenic shift and drift | Frequent mutations with variants of concern (e.g., Delta and Omicron) |
| Treatment options | Antivirals (e.g., oseltamivir and zanamivir) | Antivirals (e.g., remdesivir, molnupiravir, and Paxlovid), mAbs |
| Complications | Pneumonia and secondary bacterial infections | Pneumonia, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), and multi-organ damage |
| References | [26,27] | [28,29] |
