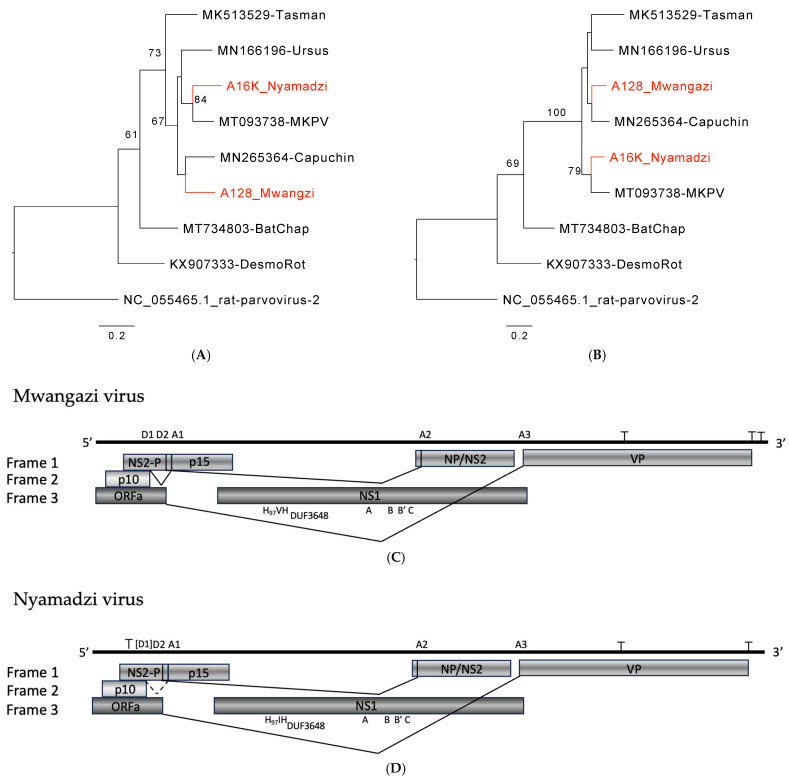
Figure 2.
Chaphamaparvoviruses from Zambia. Phylogenetic relationship of Mwangazi and Nyamadzi viruses to other viruses in the genus Chaphamaparvovirus based on NS1 (A) and VP (B) amino acid sequences. Phylogeny was reconstructed with the maximum likelihood method by applying a JTT+G4 substitution model for NS1 and a Q.yeast+F+G4 substitution model for VP1, selected by Model Finder implemented in IQtree; bootstrap values (>60%) resulting from 1000 pseudoreplicates are indicated at the respective nodes; the scale bars indicate the number of amino acid substitutions per site, and GenBank accession numbers are given next to the branches. The red font indicates viruses described in this study. (C) Schematic of Mwangazi virus genome organization. (D) Schematic of Nyamadzi virus genome organization. Gray shading indicates the three possible reading frames. Predicted major splice sites (donor sites D1, D2, and acceptor sites A1–A3), polyadenylation signals (T), SF3 helicase (H97), Walker A, B, B’, C, and domain of unknown function (DUF) 3648 motifs are indicated.