Figure 4.
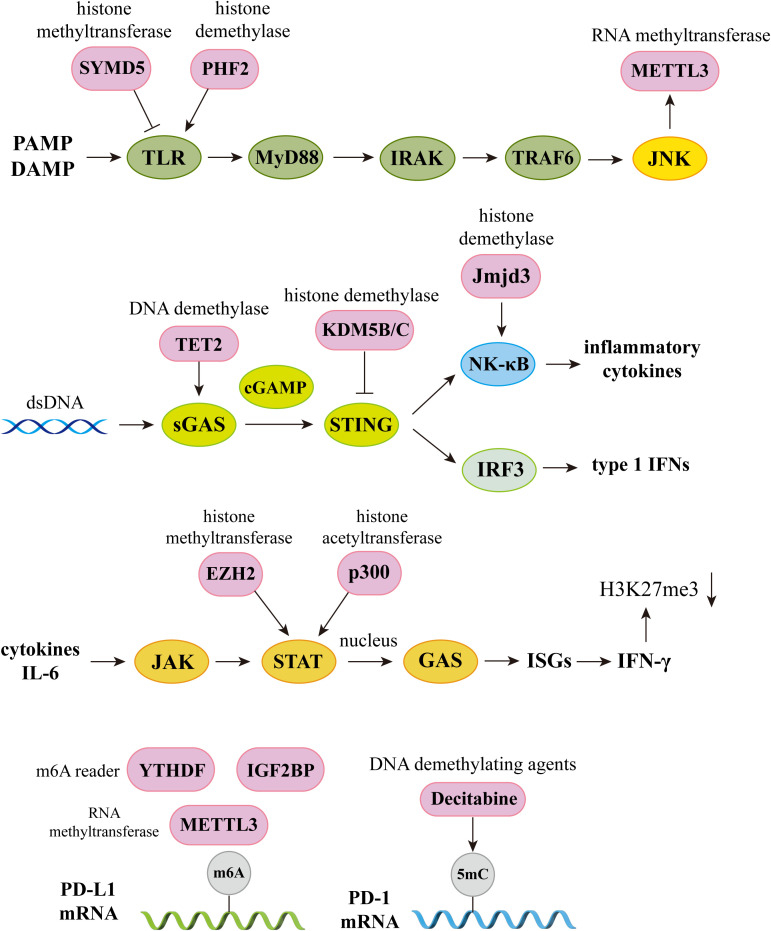
The crossroads of epigenetics and immune pathways. Epigenetics plays an integral role in the regulation of immune pathways. In the TLR signaling pathway, histone methyltransferase SYMD5 catalyzes H4K20me3 to repress TLR4 expression; histone demethylase PHF2 activates TLR4 expression by removal of H3K9me1. Knockdown of JNK will inhibit m6A and METTL3 expression; In the sGAS-STING signaling pathway, DNA demethylases TET2 elevate cGAS levels, histone demethylases KDM5B and KDM5C inhibit STING expression. Histone demethylase Jmjd3 upregulates NF-kB-mediated inflammatory cytokine levels by removal of H3K27me3; In the JAK-STAT signaling pathway, activator of transcription STAT recruits histone acetyltransferases and chromatin-remodeling enzymes, and histone methyltransferase EZH2 and histone acetyltransferase p300 elevate STAT levels. IFN-γ produced by this signaling pathway can induce H3K27me3, which is associated with gene repression; In the PD-1 and PD-L1 pathway, knockdown of METTL3 abolishes m6A modification and reduces stabilization of PD-L1 mRNA, and m6A reader IGF2BP and YTHDF regulates RNA stability and expression levels of PD-L1. DNA methyltransferase inhibitor 5-aza-2’ deoxycytidine (decitabine) enhances PD-1 expression. PAMP, pathogen associated molecular pattern; DAMP, damage associated molecular pattern; TLR, Toll-like receptors; IRAK, interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase; TRAF6, Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6; IRF3, Interferon regulatory factor 3; ISGs, Interferon-stimulated genes.
