Table 1. Optimization of Reaction Conditionsa.
| Entry | Variation of standard condition | Yieldb |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | None | 85%(E/Z = 1:2) |
| 2 | K2CO3 instead of LiOH | 29% |
| 3 | TMG instead of LiOH | 72% |
| 4 | Pd(PPh3)2Cl2 instead of Pd(PPh3)4 | 79% |
| 5 | Pd2(dba)3 instead of Pd(PPh3)4 | 19% |
| 6 | MeCN instead of THF | 43% |
| 7 | no XantPhos | 28% |
| 8 | no (o–OMe)Ph2PPh | 72% |
| 9 | no Pd(PPh3)4 | N.D. |
| 10 | in the dark | N.D. |
| 11 | no LiOH | trace |
| 12 | 0.3 mmol scale | 91%c(E/Z = 1:2) |
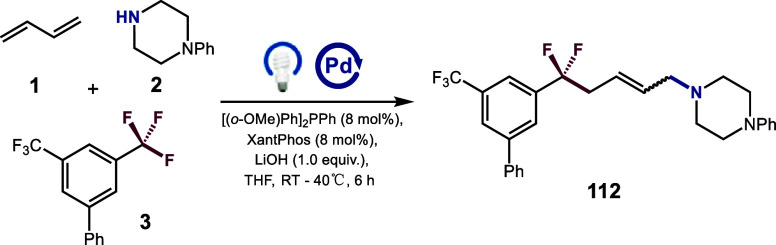
Reaction conditions: 1 (0.30 mmol), 2 (0.15 mmol), 3 (0.45 mmol), Pd(PPh3)4 (1.5 mol%), XantPhos (8 mol%), [(o-OMe)Ph]2PPh (8 mol%), LiOH (0.15 mmol), THF (0.1 M), λmax = 440 nm Kessil (40 W), N2, RT – 40 °C, 6 h.
GC yield with 1,3,5-trimethylbenzene as internal standard.
12 h, isolated yield. N.D., not detected.