Figure 3.
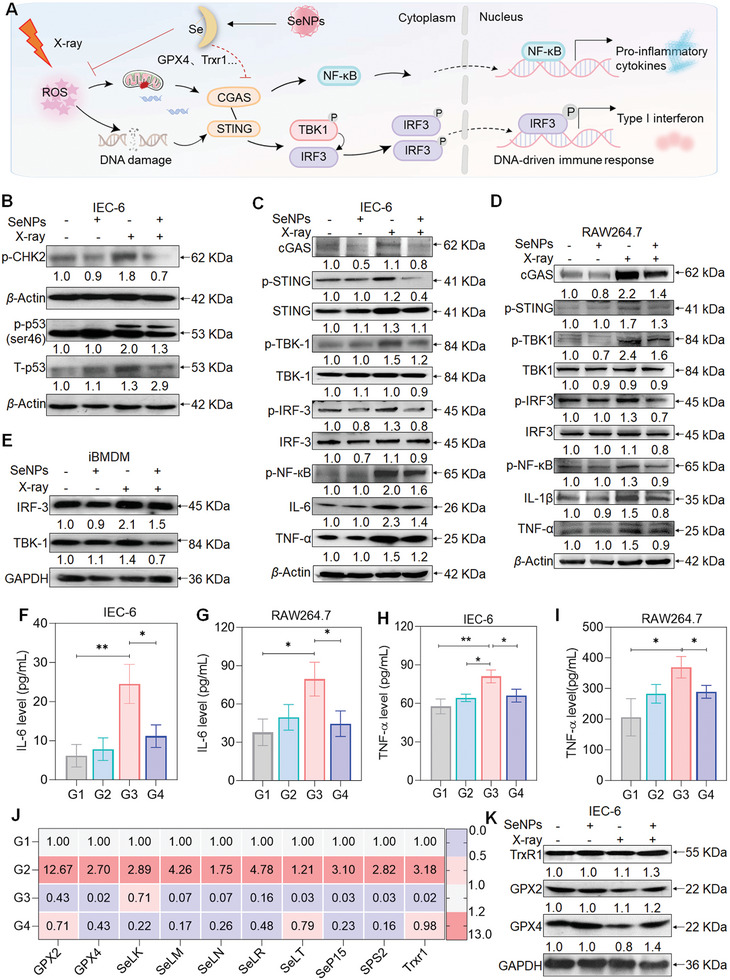
SeNPs suppressed cGAS‐STING signaling pathway activation by inducing selenoprotein expression. A) Schematic diagram of the regulatory mechanism of SeNPs inhibited cGAS‐STING signal cascade under DNA damage response. B) SeNPs inhibited X‐ray‐induced DNA damage in IEC‐6 cells. Effects of SeNPs on cGAS‐STING signaling pathway in IEC‐6 cells C), RAW264.7 cells D) and BMDMs E) upon X‐ray irradiation. Cells were pretreated with SeNPs (2 µM) for 6 h followed by X‐ray (16 Gy) irradiation and 48 h later the total protein was collected and subjected for the analysis of protein expression. F‐I) Expression of TNF‐α and IL‐6 in IEC‐6 and RAW264.7 cells was examined by ELISA assay. Data are represented as mean ± SD, n = 3. J) The mRNA level of selenoprotein in IEC‐6 cells after the treatment of SeNPs (2 µM) and X‐ray (16 Gy) (n = 3). K) Expression of GXP2, GPX4, and TrxR1 in IEC‐6 cells. Cells were pretreated with SeNPs (2 µM) for 6 h and then irradiated by X‐ray (16 Gy). After 48 h, the total protein was collected and submitted to a Western blotting assay. G1: Control, G2: SeNPs, G3: X‐ray, G4: X‐ray + SeNPs. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 are considered statistically significant differences.
