Figure 3. oAβ inhibits GIRK channel activity through PrPC-mGluR5-PLA2 activation.
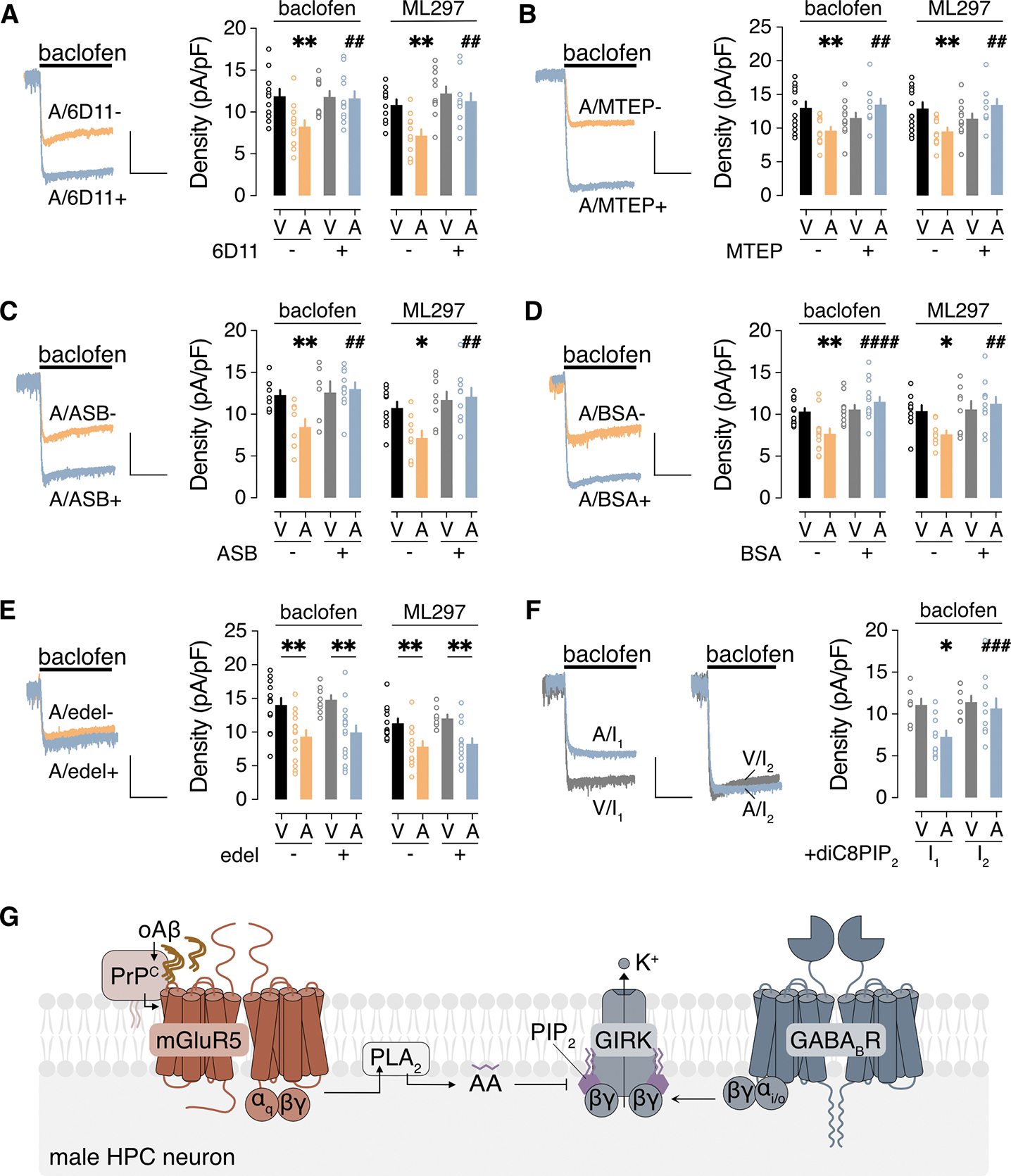
(A to F) Ibaclofen and IML297 in male HPC neurons incubated with vehicle (V) or 0.5 μM oAβ (A, 3 hours), with (+) or without (−) the indicated agents to interrogate underlying signaling mechanisms: (A) PrPC antibody 6D11 pretreatment (2.5 μg/mL for 30 min); (B) mGluR5 antagonist MTEP (10 μM); (C) PLA2 inhibitor ASB 14780 (ASB, 5 μM); (D) bovine serum albumin (BSA, fatty acid-free, 0.5 mg/mL); (E) PLC inhibitor edelfosine (edel, 10 μM); (F) PIP2 analog diC8PIP2 (25 μM) in the internal solution, measured immediately after whole-cell formation (I1) and then 90 s later (I2). Scale: 500 pA/5 s. Data are presented as mean ± SEM from 6 to 14 neurons in 3 to 4 independent cultures per condition. Data in (A to D) were analyzed by two-way ANOVA and Šídák’s multiple comparisons: *P<0.05 and **P<0.01 vs. V/-; ## P<0.01 and ####P< 0.0001 vs. A/−. Data in (E) were analyzed by two-way ANOVA and Šídák’s multiple comparisons: **P<0.01. Data in (F) were analyzed by two-way ANOVA with repeated measures and Šídák’s multiple comparisons: *P<0.05 vs. V/I1; ###P<0.001 vs. A/I1. (G) Schematic of the signaling pathway underlying the oAβ-induced suppression of GIRK-dependent signaling in male HPC neurons.
