Abstract
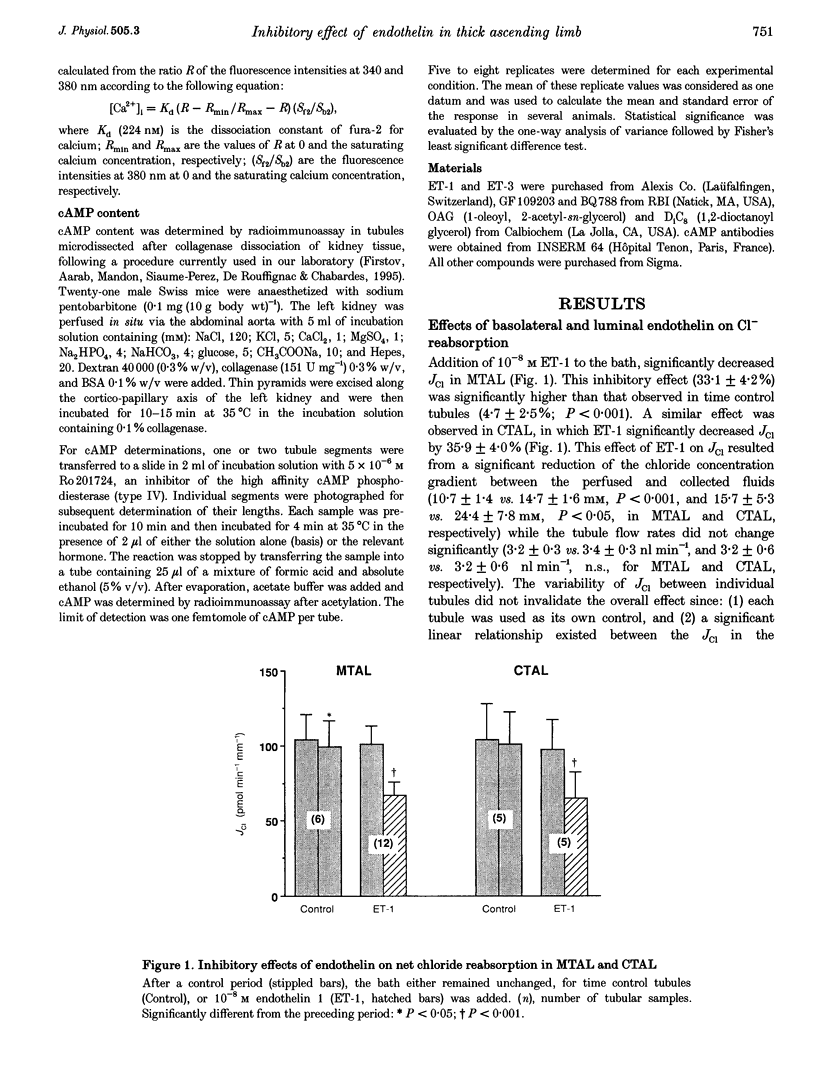
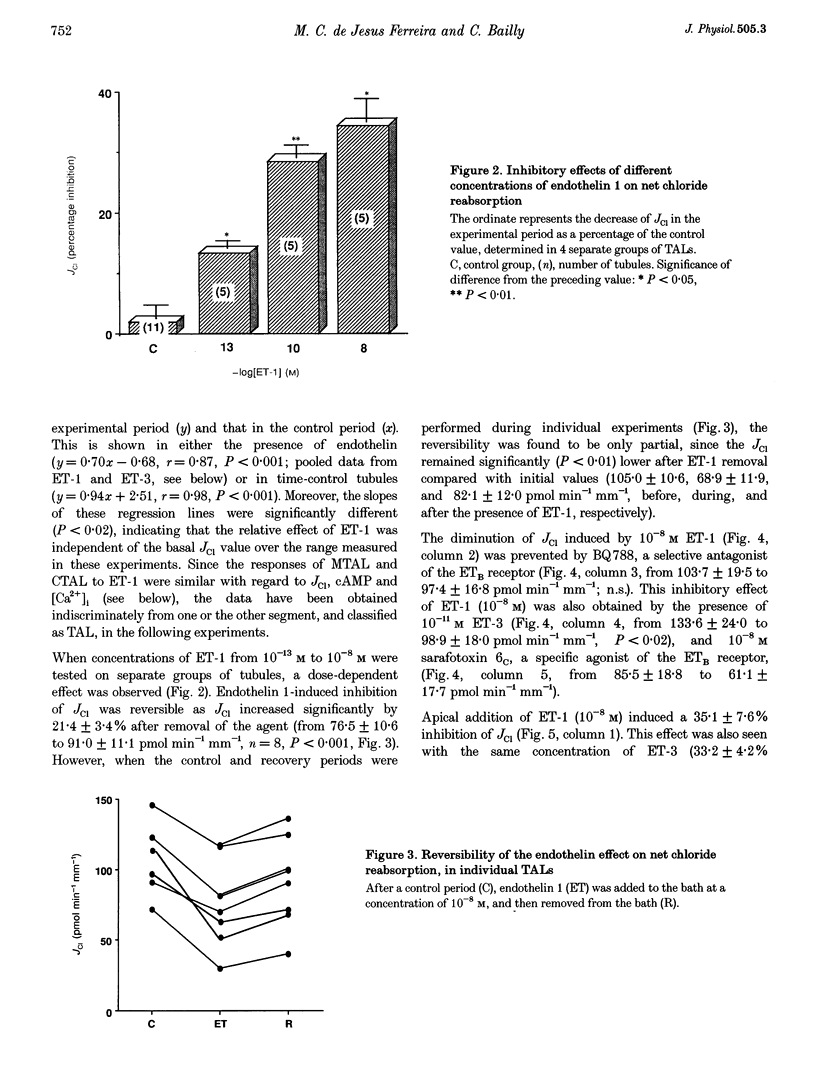
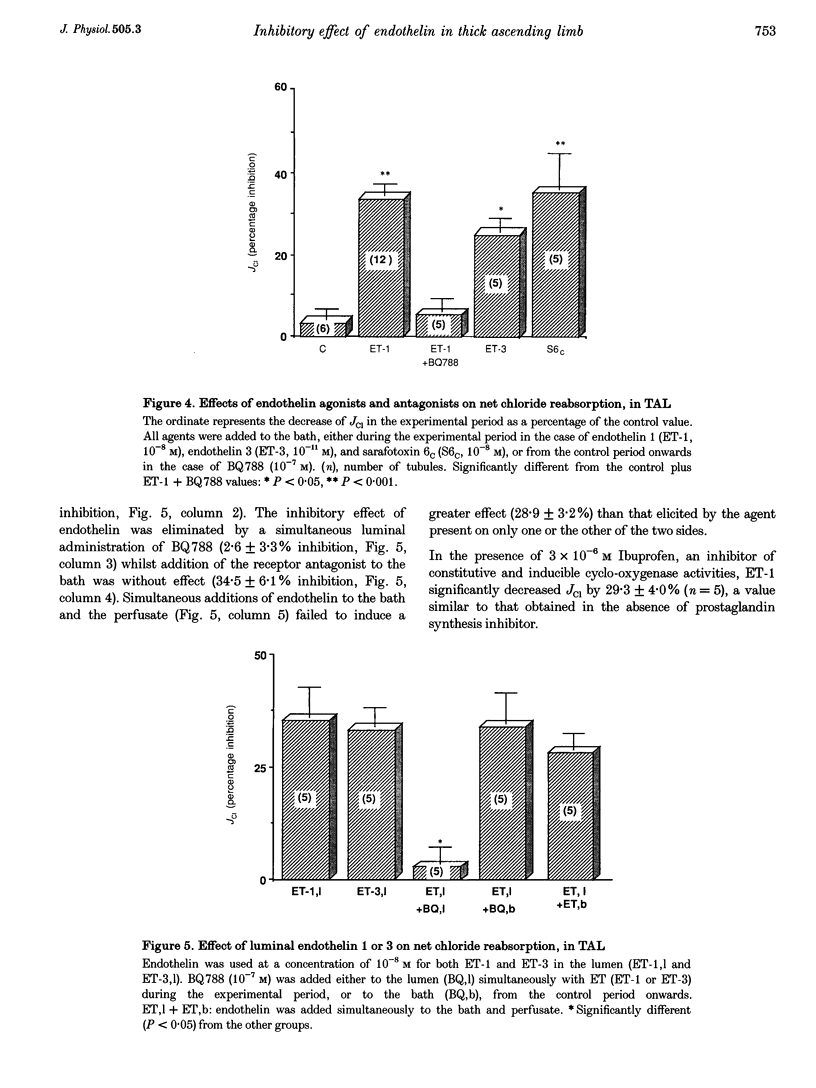
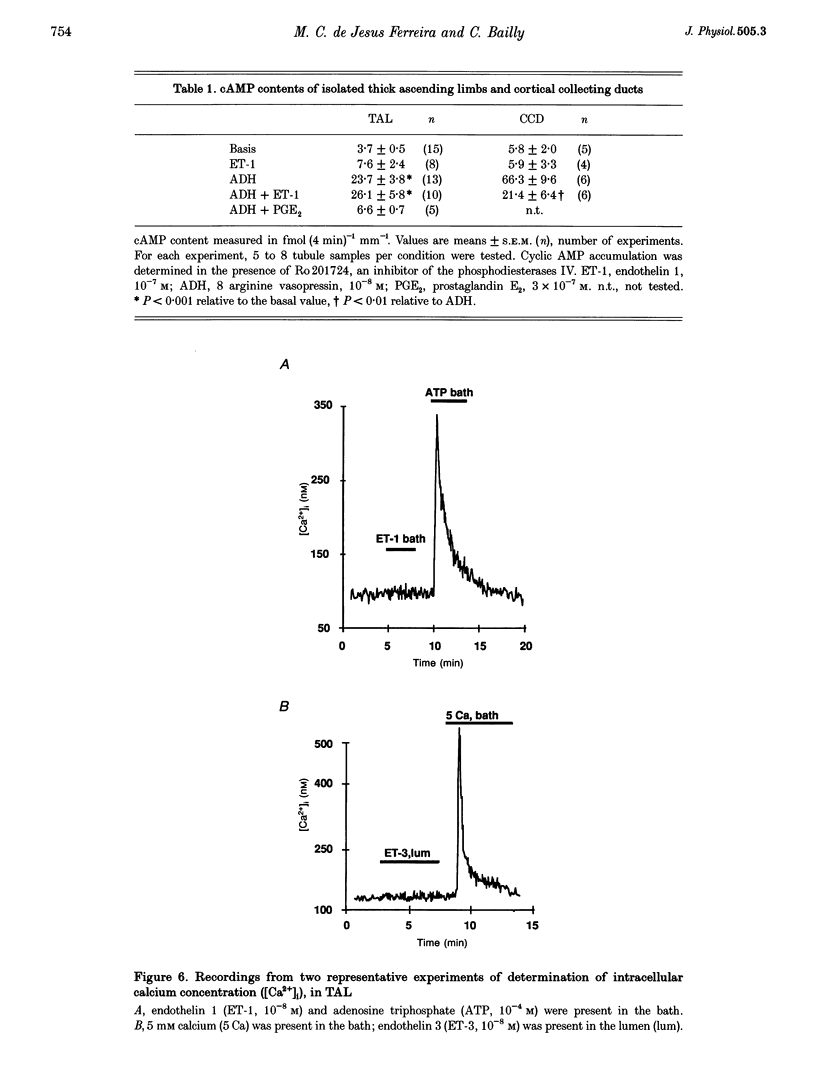
1. The recent localization of endothelin synthesis and receptors in the thick ascending limb (TAL) prompted us to investigate a possible autocrine and/or paracrine effect of this agent. The net chloride flux (JCl) has been determined in isolated cortical and medullary TALs by the in vitro microperfusion technique. 2. In both segments, endothelin 1 (ET-1) at 10(-8) M in the bath significantly decreased JCl, an effect which was partially reversible and observed at concentrations equal to or greater than 10(-13) M. 3. This JCl inhibition (by 33.9 +/- 3.2%) was blocked by BQ788 and was also observed with sarafotoxin 6C and ET-3, indicating that endothelin receptor B (ETB) are present in TAL. 4. ET-1 did not affect cAMP content under basal or hormone-stimulated conditions. The presence of a prostaglandin synthesis inhibitor also did not prevent the ET-1 action on JCl. 5. The ET-1-induced inhibition of JCl was prevented by protein kinase C inhibitors (staurosporine or GF 109203) and was reproduced by diacylglycerol analogues (OAG and DiC8). However, ET-1 failed to increase intracellular Ca2+ concentration. 6. Addition of ET-1 or ET-3 to the apical surface induced a decrease of JCl throgh ETB receptors, an effect which was not additive with that induced by basolateral ET-1, and was not concomitant with an increase in intracellular Ca2+ concentration. 7. It is concluded that the basolateral and luminal inhibitions of JCl by ET-1 in TAL, through ETB receptors, is mediated by a protein kinase C activation which is independent of intracellular Ca2+ increase.
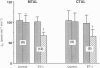
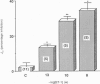
Full text
PDF





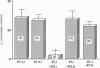
Images in this article
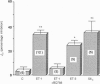
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Badr K. F., Murray J. J., Breyer M. D., Takahashi K., Inagami T., Harris R. C. Mesangial cell, glomerular and renal vascular responses to endothelin in the rat kidney. Elucidation of signal transduction pathways. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jan;83(1):336–342. doi: 10.1172/JCI113880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldi E., Musial A., Kester M. Endothelin stimulates phosphatidylcholine hydrolysis through both PLC and PLD pathways in mesangial cells. Am J Physiol. 1994 Jun;266(6 Pt 2):F957–F965. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1994.266.6.F957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burg M., Grantham J., Abramow M., Orloff J. Preparation and study of fragments of single rabbit nephrons. Am J Physiol. 1966 Jun;210(6):1293–1298. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.210.6.1293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champigneulle A., Siga E., Vassent G., Imbert-Teboul M. V2-like vasopressin receptor mobilizes intracellular Ca2+ in rat medullary collecting tubules. Am J Physiol. 1993 Jul;265(1 Pt 2):F35–F45. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1993.265.1.F35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow L. H., Subramanian S., Nuovo G. J., Miller F., Nord E. P. Endothelin receptor mRNA expression in renal medulla identified by in situ RT-PCR. Am J Physiol. 1995 Sep;269(3 Pt 2):F449–F457. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1995.269.3.F449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firsov D., Aarab L., Mandon B., Siaume-Perez S., de Rouffignac C., Chabardès D. Arachidonic acid inhibits hormone-stimulated cAMP accumulation in the medullary thick ascending limb of the rat kidney by a mechanism sensitive to pertussis toxin. Pflugers Arch. 1995 Mar;429(5):636–646. doi: 10.1007/BF00373984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firth J. D., Schricker K., Ratcliffe P. J., Kurtz A. Expression of endothelins 1 and 3 in the rat kidney. Am J Physiol. 1995 Oct;269(4 Pt 2):F522–F528. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1995.269.4.F522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia N. H., Garvin J. L. Endothelin's biphasic effect on fluid absorption in the proximal straight tubule and its inhibitory cascade. J Clin Invest. 1994 Jun;93(6):2572–2577. doi: 10.1172/JCI117268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guntupalli J., DuBose T. D., Jr Effects of endothelin on rat renal proximal tubule Na(+)-Pi cotransport and Na+/H+ exchange. Am J Physiol. 1994 Apr;266(4 Pt 2):F658–F666. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1994.266.4.F658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knotek M., Jaksić O., Selmani R., Skorić B., Banfić H. Different endothelin receptor subtypes are involved in phospholipid signalling in the proximal tubule of rat kidney. Pflugers Arch. 1996 Jun;432(2):165–173. doi: 10.1007/s004240050120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohan D. E., Padilla E., Hughes A. K. Endothelin B receptor mediates ET-1 effects on cAMP and PGE2 accumulation in rat IMCD. Am J Physiol. 1993 Nov;265(5 Pt 2):F670–F676. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1993.265.5.F670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin E. R., Marsden P. A., Brenner B. M., Ballermann B. J. Identification and characterization of endothelin binding sites in rat renal papillary and glomerular membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Jul 14;162(1):130–137. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91972-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadler S. P., Zimpelmann J. A., Hébert R. L. Endothelin inhibits vasopressin-stimulated water permeability in rat terminal inner medullary collecting duct. J Clin Invest. 1992 Oct;90(4):1458–1466. doi: 10.1172/JCI116013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naruse M., Uchida S., Ogata E., Kurokawa K. Endothelin 1 increases cell calcium in mouse collecting tubule cells. Am J Physiol. 1991 Oct;261(4 Pt 2):F720–F725. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1991.261.4.F720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neant F., Bailly C. Luminal and intracellular cGMP inhibit the mTAL reabsorptive capacity through different pathways. Kidney Int. 1993 Oct;44(4):741–746. doi: 10.1038/ki.1993.308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Néant F., Imbert-Teboul M., Bailly C. Cyclic guanosine monophosphate is the mediator of platelet-activating factor inhibition on transport by the mouse kidney thick ascending limb. J Clin Invest. 1994 Sep;94(3):1156–1162. doi: 10.1172/JCI117431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostlund E., Mendez C. F., Jacobsson G., Fryckstedt J., Meister B., Aperia A. Expression of protein kinase C isoforms in renal tissue. Kidney Int. 1995 Mar;47(3):766–773. doi: 10.1038/ki.1995.117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulais M., Baudouin-Legros M., Teulon J. Extracellular ATP and UTP trigger calcium entry in mouse cortical thick ascending limbs. Am J Physiol. 1995 Mar;268(3 Pt 2):F496–F502. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1995.268.3.F496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulais M., Baudouin-Legros M., Teulon J. Functional evidence for a Ca2+/polyvalent cation sensor in the mouse thick ascending limb. Am J Physiol. 1996 Nov;271(5 Pt 2):F1052–F1060. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1996.271.5.F1052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokolovsky M. Endothelin receptor subtypes and their role in transmembrane signaling mechanisms. Pharmacol Ther. 1995;68(3):435–471. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(95)02015-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terada Y., Tomita K., Nonoguchi H., Marumo F. Different localization of two types of endothelin receptor mRNA in microdissected rat nephron segments using reverse transcription and polymerase chain reaction assay. J Clin Invest. 1992 Jul;90(1):107–112. doi: 10.1172/JCI115822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terada Y., Tomita K., Nonoguchi H., Yang T., Marumo F. Expression of endothelin-3 mRNA along rat nephron segments using polymerase chain reaction. Kidney Int. 1993 Dec;44(6):1273–1280. doi: 10.1038/ki.1993.379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomita K., Nonoguchi H., Marumo F. Effects of endothelin on peptide-dependent cyclic adenosine monophosphate accumulation along the nephron segments of the rat. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jun;85(6):2014–2018. doi: 10.1172/JCI114667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomita K., Nonoguchi H., Marumo F. Inhibition of fluid transport by endothelin through protein kinase C in collecting duct of rats. Contrib Nephrol. 1991;95:207–215. doi: 10.1159/000420661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomita K., Nonoguchi H., Terada Y., Marumo F. Effects of ET-1 on water and chloride transport in cortical collecting ducts of the rat. Am J Physiol. 1993 Apr;264(4 Pt 2):F690–F696. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1993.264.4.F690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torikai S., Kurokawa K. Effect of PGE2 on vasopressin-dependent cell cAMP in isolated single nephron segments. Am J Physiol. 1983 Jul;245(1):F58–F66. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1983.245.1.F58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ujiie K., Terada Y., Nonoguchi H., Shinohara M., Tomita K., Marumo F. Messenger RNA expression and synthesis of endothelin-1 along rat nephron segments. J Clin Invest. 1992 Sep;90(3):1043–1048. doi: 10.1172/JCI115918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter R., Helmle-Kolb C., Forgo J., Binswanger U., Murer H. Stimulation of Na+/H+ exchange activity by endothelin in opossum kidney cells. Pflugers Arch. 1995 May;430(1):137–144. doi: 10.1007/BF00373849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkes B. M., Ruston A. S., Mento P., Girardi E., Hart D., Vander Molen M., Barnett R., Nord E. P. Characterization of endothelin 1 receptor and signal transduction mechanisms in rat medullary interstitial cells. Am J Physiol. 1991 Apr;260(4 Pt 2):F579–F589. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1991.260.4.F579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]