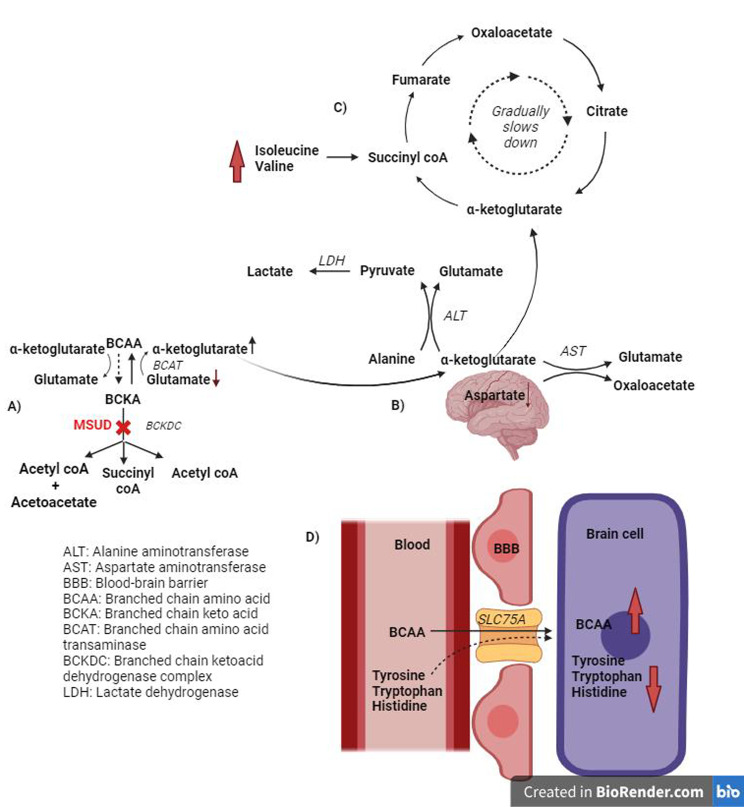
Fig. 3.
Biochemical changes in MSUD: (A) Enzyme defect in MSUD causes accumulation of ketoacids and reverse flux reaction producing increased α-ketoglutarate; (B) α-ketoglutarate is converted to glutamate and respective products via aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase; (C) α-ketoglutarate, thus produced is quickly utilized in the Kreb’s cycle via anaplerotic role of isoleucine and valine by production of succinyl coA; (D) BCAA competes with other amino acids that utilize the same transporter to enter into brain cells