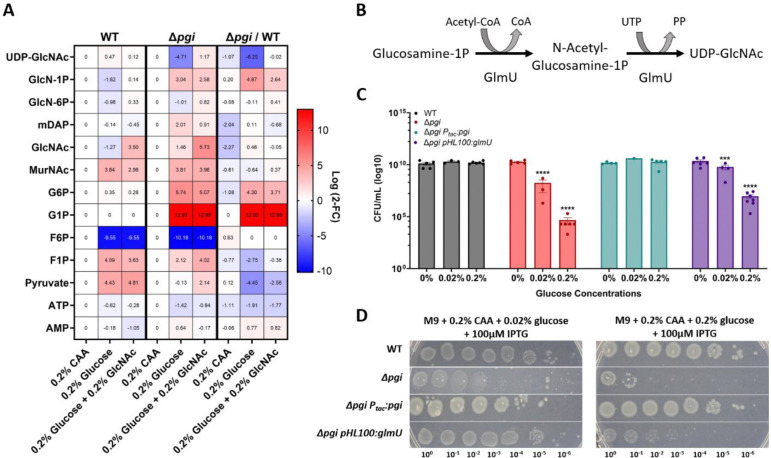
Figure 4: Targeted metabolomics of Δpgi reveal bottleneck around GlmU activity.
A) Heatmaps normalized to strain specific casamino acids conditions. The right column represents the change between strains in the indicated conditions. Log2 fold change is shown on the right side of the maps. B) The enzymatic reaction of GlmU. The acetyltransferase activity catalyzes N-acetylglucosamine-1P from glucosamine-1P and Acetyl-CoA. The second step is the uridyltransferase reaction which adds UDP onto GlcNAc, forming the end-product UDP-GlcNAc. C) Overnight cultures were serially diluted and spot-plated on MM agar with the indicated additions of percent glucose and 200uM IPTG. At least 4 independent replicates are presented, with raw data points and SEM. *** = p<0.001, ****=p<0.0001 (2-way ANOVA). Δpgi was compared against WT values and Δpgi pHL100: glmU was compared against Δpgi. D) The indicated strains were grown overnight in M9 + casamino acids and the diluted and spot-plated on M9 agar plates containing CAA and the indicated glucose concentration.