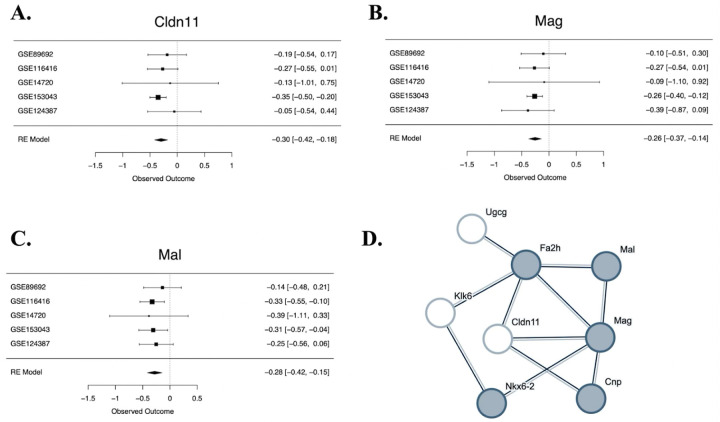
Figure 2. Genes within a network focused on oligodendrocyte differentiation are differentially expressed in early life stress models.
A-C. Forest plots for two differentially expressed genes from the meta-analysis (FDR<0.05: Cldn11 & Mag), and a third gene that shows a trend towards differential expression (FDR<0.10: Mal) that are all part of a network related to oligodendrocyte differentiation. Rows illustrate ELS Log2FC (squares) with 95% confidence intervals (whiskers) for each of the datasets and the meta-analysis random effects model (“RE Model”). Forest plots allow for visual inspection of the consistency and magnitude of effects across the five studies. A. A forest plot showing the down-regulation of claudin 11(Cldn11) in ELS models. B. A forest plot showing the down-regulation of myelin-associated glycoprotein (Mag) in ELS models. C. A forest plot showing the trend towards a down-regulation of mal, T cell differentiation protein (Mal) in early life stress models. D. Multiple top differentially expressed genes are found in the same predicted protein-protein interaction (PPI) network enriched for genes associated with oligodendrocyte differentiation. To create the PPI network, top genes from the meta-analysis (p<0.001: 40 genes) were entered into the StringDB database. The only identifiable network (cluster) of 8 genes included six genes with either significant differential expression in ELS models (FDR<0.05: Mag, Cldn11) or a non-significant trend towards differential expression in ELS models (FDR<0.10: Mal, Fa2h, Klk6, Ugcg). The nodes represent proteins and are labeled with mouse gene symbol annotation. The lines represent predicted protein-protein associations. The associations are meant to be specific and meaningful (proteins jointly contribute to a shared function), but this does not necessarily mean they are physically binding to each other. The shaded nodes (grey) were identified as being part of a gene set involved in oligodendrocyte differentiation (GO:0048709) that was enriched with differential expression. Other genes within the network are part of a gene set involved in Central nervous system myelination (GO:0022010) that was also enriched with differential expression (including Klk6), or have also been previously associated with oligodendrocyte function and myelination (Cldn11).