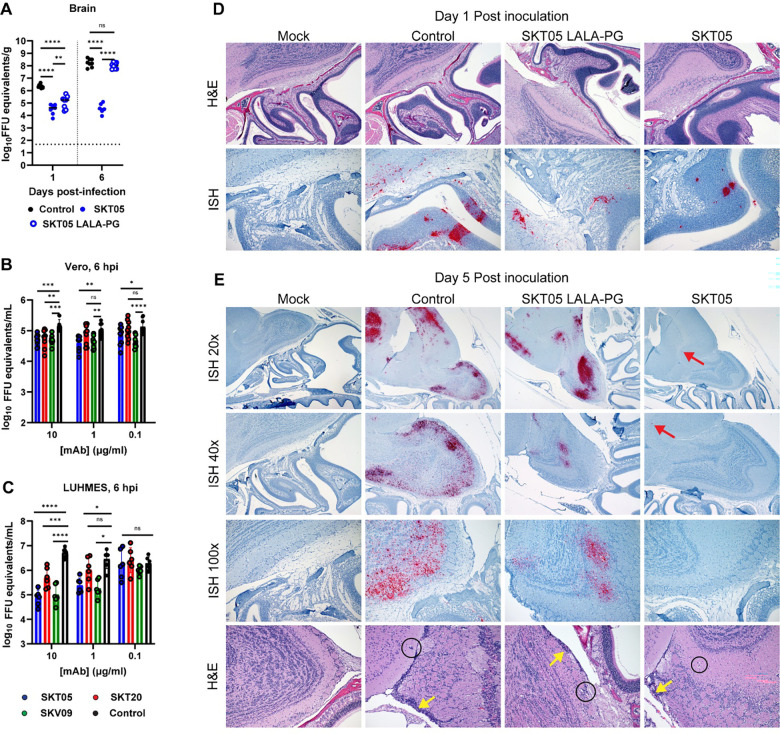
Figure 5. SKT05 limits neuroinvasion and spread into the brain through inhibition of viral egress.
(A) C3H/HeN mice were treated with 200 μg of SKT05, SKT05-LALA-PG, or a control one day prior to infection with TC-83. At 1 and 6 dpi, viral loads were determined in the brains by RT-qPCR (n = 8/group; 2 independent experiments). The median is represented, and the dotted line indicates the LOD of the assay. Statistical significance was determined by one-way ANOVA with Holm-Sidak’s post-test. (B-C) Viral egress inhibition by indicated mAbs was evaluated in Vero cells (B) and LUHMES (C). Supernatants were collected at 6 hpi to quantify viral RNA by RT-qPCR. Data is representative of the mean ± SD of 2–3 independent experiments performed in triplicate. Statistical significance was determined by two-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post-test comparing all groups to the isotype control. (D-E) C3H/HeN mice were pre-treated with 200 μg of SKT05, SKT05-LALA-PG, or a control antibody one day before infection with TC-83. At 1 and 5 dpi, skulls with brains intact were harvested, fixed, then decalcified before paraffin embedding and sectioning. Representative images of sagittal skull and brain sections stained for VEEV RNA by in situ hybridization (ISH) or with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E). The red arrows point out focal vRNA staining, the yellow arrows indicate meningitis, and the circles indicate perivascular cuffing. Data are representative images of two independent experiments (n = 6 – 8/group).