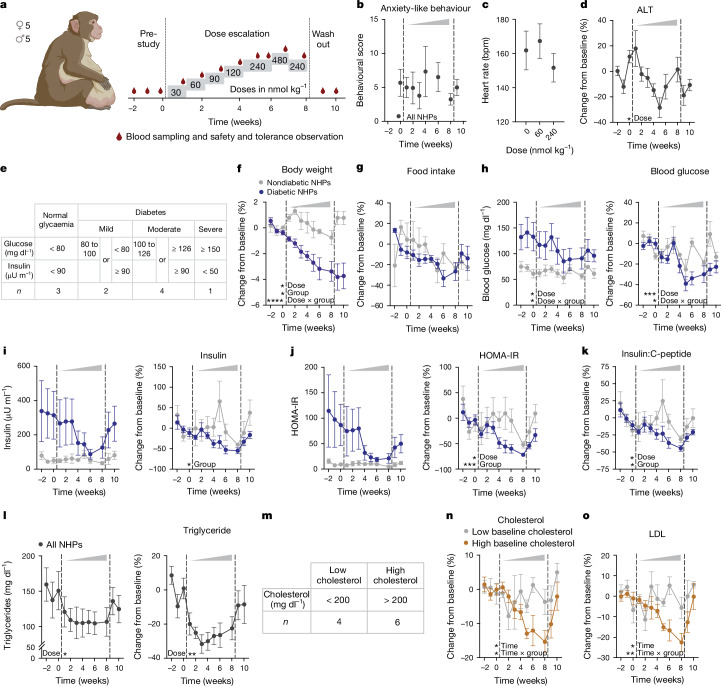
Fig. 5. NK2R agonism safely counteracts cardiometabolic disease in diabetic, obese macaques.
a, Schematic of EB1001 dose-escalation study in rhesus macaques (nonhuman primates (NHPs)). b–d, Anxiety-like behaviour (b), heart rate (c) and blood alanine transaminase concentration over the course of the dose-escalation study (n = 10 macaques). e, Stratification of macaque groups on the basis of diabetic status. f–k, Changes in body weight (f), food intake (g), fasting blood glucose (h), insulin level (i), HOMA-IR (j) and insulin:C-peptide ratio (k) for normoglycaemic (n = 3) and diabetic (n = 7) macaques. All plot colours as in key in f. l, Changes in triglyceride concentrations for all macaques over the course of the study (n = 10 macaques). m–o, Stratification of macaque groups on the basis of baseline cholesterol levels (m) and changes in total cholesterol (n) and LDL cholesterol (o) over the course of the dose escalation. All plot colours as in key in n. n = 4 macaques (low baseline cholesterol), n = 6 macaques (high baseline cholesterol). Data are mean ± s.e.m. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.005, ****P < 0.0001. Detailed statistics are in the Supplementary Information and Source Data.