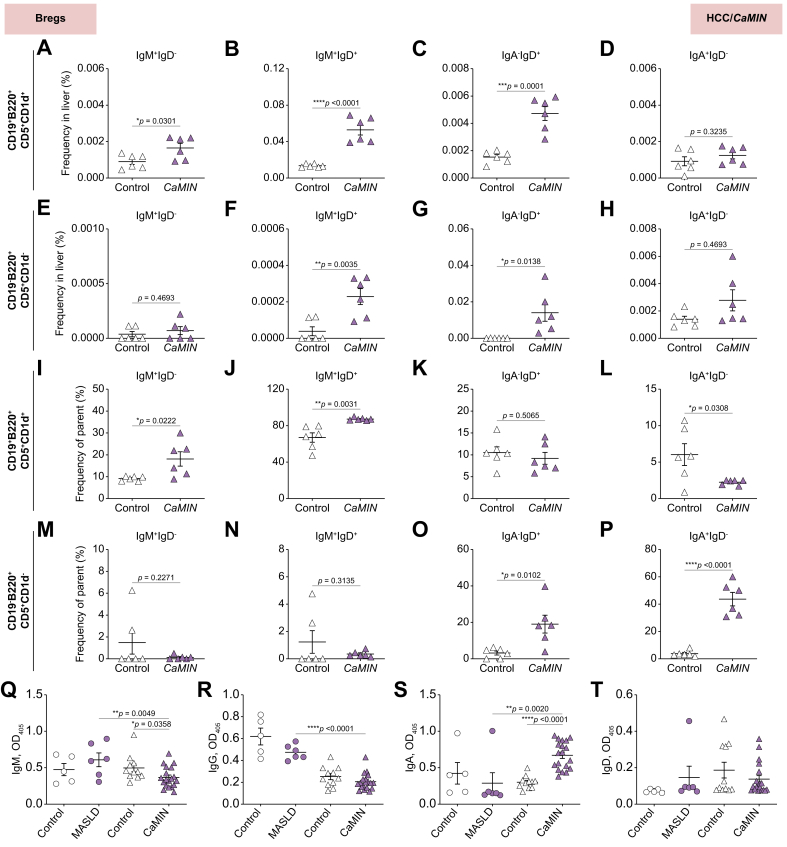
Fig. 3.
Upregulation of IgM+- and IgD+-expressing CD19+B220+CD5+CD1d+ and CD19-B220+CD5+CD1d- Bregs in the livers of HCC/CaMIN mice.
(A–D) Frequencies of (A) IgM+IgD--, (B) IgM+IgD+-, (C), IgA-IgD+-, and (D) IgA+IgD--expressing CD19+B220+CD5+CD1d+ Bregs. (E–H) Frequencies of (E) IgM+IgD--, (F) IgM+IgD+-, (G) IgA-IgD+-, and (H) IgA+IgD--expressing CD19-B220+CD5+CD1d- Bregs. (I–L) Percentage of (I) IgM+IgD-, (J) IgM+IgD+, (K), IgA-IgD+, and (L) IgA+IgD- among CD19+B220+CD5+CD1d+ Bregs. (M–P) Percentage of (M) IgM+IgD-, (N) IgM+IgD+, (O), IgA-IgD+, and (P) IgA+IgD- among CD19-B220+CD5+CD1d- Bregs. (Q–T) ELISA to determine the levels of (Q) IgM, (R) IgG, (S) IgA and (T) IgD in the plasma samples of mice with MASLD and HCC/CaMIN. The data were analyzed using the unpaired Student’s t test. The data are shown as the mean ± SEM, n = 6. ∗p <0.05, ∗∗p <0.01, ∗∗∗p <0.001, ∗∗∗∗p <0.0001. Fig. S3 shows the MASLD and HCC/NRASG12V/p19Arf-/- models. Bregs, B regulatory cells; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; MASLD, metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease.