Fig. 8.
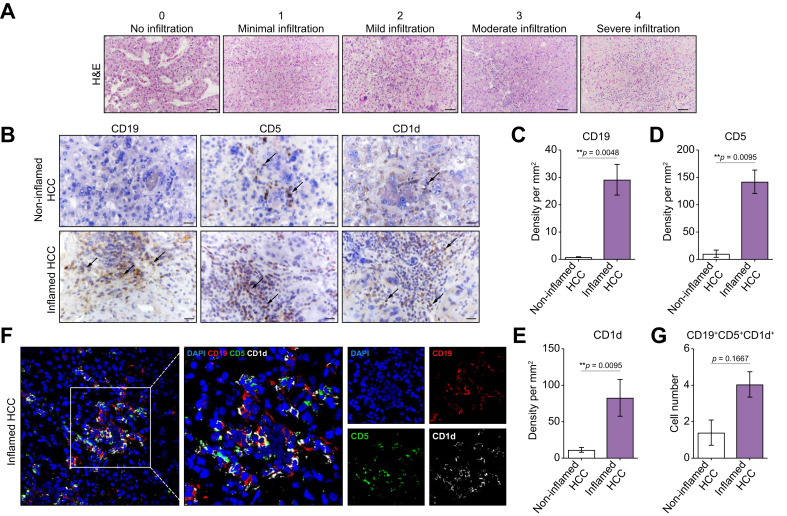
The inflamed subtype of human HCC is characterized by the presence of high numbers of CD19+-, CD5+-, and CD1d+-expressing B cells.
(A) Representative H&E images of human HCC liver tissues and immune infiltration assessment scores (non-inflamed HCC [≤2 infiltration score]; inflamed HCC [≥3 infiltration score]). (B) Representative images of IHC of CD19, CD5, and CD1d expression in non-inflamed and inflamed human HCC tissues. Scale bar, 100 μm. (C–E) Density of cellular markers (C) CD19, (D) CD5, and (E) CD1d in human non-inflamed and inflamed HCC tissues. The data were analyzed using the Mann‒Whitney nonparametric test, n = 10. ∗∗p <0.01. (F) Representative IF images of frozen liver sections from patients with inflamed HCC stained with CD19 (red), CD5 (green), and CD1d (white) antibodies and counterstained with DAPI (blue). (G) Quantification of CD19+CD5+CD1d+ B cells in human non-inflamed and inflamed HCC tissues. The data were analyzed using the Mann‒Whitney nonparametric test, n = 7. ∗∗p <0.01. HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; IHC, immunohistochemistry; IF, immunofluorescence.