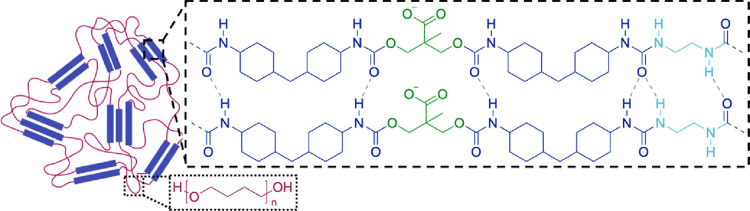
Figure 1.
Schematic of polyurethane architecture, based on the polymer composition used in this work, separated into hydrogen-bonding “hard blocks” [comprising diisocyanate (hydrogenated methylene diphenyl diisocyanate, blue), a charge-stabilizing hydrophilic unit (dimethylolpropionic acid, green), and a diamine chain extender (ethylenediamine, turquoise)] and a long-chain polyether soft segment [poly(tetramethylene oxide), purple]. The formation of hydrogen bonds between urethane and urea groups is shown by gray dashed lines.