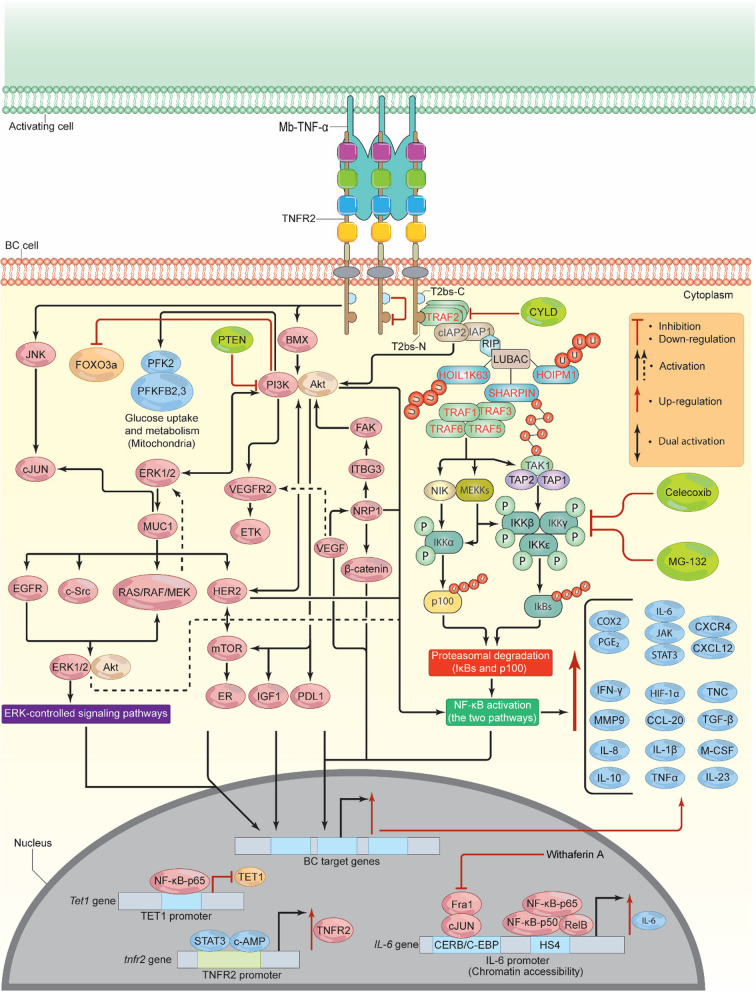
Fig. 4.
TNFR2/Mb-TNF-α signalosome pathway. Upon Mb-TNF-α binding to TNFR2, the T2bs-N region recruits TRAF2, which then recruits E3 ligases (cIAP1, cIAP2, RIP, and LUBAC). LUBAC attaches M1-linked ubiquitin chains, stabilizing the signaling complex and enhancing downstream signaling. This leads to the accumulation of TRAFs 1, 3, 5, and 6, which phosphorylate TRAF 3, releasing NIK. NIK stimulates MEKK1, 2, 3, and TAK1, which then phosphorylate, IKKα, IKKβ, IKKε, and KKγ, inducing NF-κB pathways. Inhibitors like Celecoxib, CYLD, and MG-132 can prevent NF-κB activation. In addition, cIAP1 and cIAP2 stimulate BMX and JNK/cJUN, which induce PI3K/Akt, resulting in the activation and phosphorylation of several pathways (ETK/VEGFR2, ERK1/2, IGF1, HER2, mTOR, NF-κB, FOXO3a, and PD-L1). HER2 and ERK1/2 induce positive feedback loop signals, which enhance BC cell metabolism and proliferation via NF-κB, c-MYC, STATs, SAP-1a, AP-1, Elk-1, Cyclin D1, and ER. TNFR2 also stimulates HIF-1α, which in turn activates VEGF and its associated signaling pathways, leading to NF-κB-p65 activation. TNFR2 in its promoter contains binding sites for both STAT3 and c-AMP, the binding of which induces TNFR2 overexpression. Epigenetically, TNFR2 enhances IL-6 overexpression and down-regulates TET1 expression. As a result of TNFR2 activation, multiple proteins will be stimulated (CCL-2, PDL-1, IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, IL-23, M-CSF, MMP-9, COX-2/PGE2, TGF-β, CXCR4/CXCL-12, TNF-α, TNC, IFN-γ, and HIF-1α), leading to drug resistance, altered metabolism, migration, invasion, and the development of EMT. TNFR2, tumor necrosis receptor type 2; Mb-TNF-α, membrane-bound tumor necrosis factor; TRAF, TNF receptor associated factor; T2bs-C, TRAF2-binding site C; T2bs-N, TRAF2-binding site N; cIAP, cellular inhibitor of apoptosis; SHARPIN, shank-associated RH domain-interacting protein; HOIL-1-K63-Ub, heme-oxidized IRP2 ubiquitin ligase 1; HOIP-M1-Ub, HOIL-1-interacting protein; LUBAC, linear ubiquitin chain assembly complex; NIK, activate NF-κB inducing kinase; MEKK, MAP kinase/ERK kinase; TAK1, transforming growth factor-activated kinase 1; TAP, TAK1-binding protein complex; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinases; Akt, protein kinase B/serine-threonine kinase; CYLD, cylindromatosis; PFK-2, phosphofructokinase-2; PFKFB2, 3, 6-phosophofrcto-2-kinase/fructose-2, 6-biphosphatase 3; mTOR, mammalian (or mechanistic) target of rapamycin; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; PTEN, phosphatase and tensin homolog; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; ETK, endothelial/epithelial tyrosine kinase; BMX, marrow x-linked kinase; VEGFR2, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2; EMT, epithelial-mesenchymal transition; MMP-9, matrix metalloproteinase-9; FOXO3a, forkhead box O3a; JNK, c-jun N-terminal kinase; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; MUC-1 and MUC1-C, Mucin; c-MYC, cellular myelocytomatosis; STAT, signal transducer and activator of transcriptions; AP-1, activator protein-1; IL-6, interleukin 6; IL-8, interleukin 8; IL-10, interleukin 10; IL-23, interleukin 23, M-CSF, macrophage colony stimulating factor; TET, ten-eleven translocation; COX-2, cyclooxygenase-2; PGE2, prostaglandin E2; TGF-β, transforming-growth factor β; IFN-γ, interferon gamma; HIF-1α, hypoxia inducible factor 1 alpha; NRP-1, Neuropilin-1; TNC, Tenascin C; ITBG3, integrin 3; FAK, focal adhesion kinase pathway; IKKs, IκB kinases; IGF1, insulin-like growth factor 1; HER2, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2