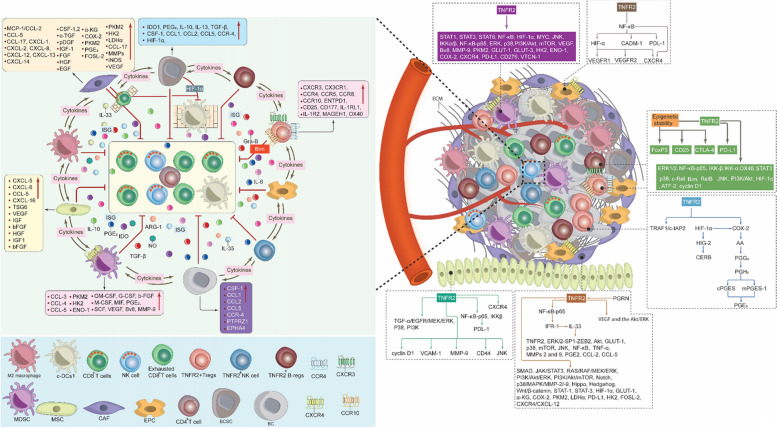
Fig. 9.
TNFR2 expression in BC TME. TNFR2+ cells secrete IL-10, IL-4, IL-6, IL-33, IL-35, TGF-β, HIF-1α, IDO, COX-2/PGE2, ARG-1, iNOS, and others, establishing the ISG. This ISG depletes essential amino acids, impairs MHC class I antigen presentation, leading to suppression of DC1s, CD8+ T cells and promoting CD8+ T cell exhaustion. COX-2/PGE2 inhibits NK cell effector receptors and induces M2 macrophage differentiation, further enhancing immunosuppression. Hypoxia-induced HIF-1α supports BC metabolism and immunosuppressive cells, inhibits NK cell cytotoxicity, and promotes MDSC differentiation, as well as induces the activation of COX-2/PGE2, IL-6, IL-10, and TGF-1β, leading to PD-L1 overexpression, which inhibits c-DC1s. TNFR2 also induces the expression of immunosuppressive receptors and stabilizes FoxP3. In CAFs, TNFR2 activation leads to stromal mass formation, hindering CD8+ T cell infiltration, and also augments AICD- and FAS-mediated cell death. TNFR2-mediates the expression of chemokines, and their receptors recruit c-DC1s to BC TME, initiating their suppression and affecting CD8+ T cell stimulation. Wnt/β-catenin downregulates CCL-4, inhibiting c-DCs1 migration, recruitment, and tumor infiltration. Moreover, increased BC cell mass and reduced blood vessel formation act as physical barriers, hindering the infiltration and recruitment of c-DC1 cells into the TME. CXCR-3+T-regs compete with CD8+ T cells for the CXCL-9 gradient, restricting their activation by c-DCs1. Immunosuppressive cells can also mediate cell-to-cell contact inhibition via PD-L1, PD-1, FAS, and CTLA-4 expression. Collectively, this can lead to dysfunctional c-DC1s, ultimately limiting their presence in the TME and supporting BC growth. TNFR2, tumor necrosis factor receptor type two; Mb-TNF-α, membrane-bound tumor necrosis factor; c-DC1, type 1 conventional dendritic cells; BC, breast cancer; BCSCs, breast cancer stem cells; IL-4, interleukin 4; IL-6, interleukin 6; IL-10, interleukin 10; IL-12, interleukin 12; IL-33, interleukin 33; IL-35, interleukin IL-35; TGF-β, transforming-growth factor β; COX-2, cyclooxygenase-2; HIF-1α, hypoxia inducible factor 1 alpha; PEG2, prorstaglandin-E2; ARG-1, arginase-1; MMP-9, matrix metalloproteinase-9; CCL-4, chemokine (C–C) motif ligand 4; CCL-19, chemokine (C–C) motif ligand 19; CCL-21, chemokine (C–C) motif ligand 21; CXCR3, C-X-C chemokine receptor 3; CXCR4, C-X-C chemokine receptor 4; XCR1, X-C motif chemokine receptor 1; CCR-5, C–C chemokine receptor type 5; CCR-7, C–C chemokine receptor type 7; IFN-γ, interferon gamma; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; PD-1, programmed cell death 1; PD-L1, programmed cell death ligand 1; CTLA-4, cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen 4; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; MHC-1, major histocompatibility complex class I; ISG, immunosuppressive gradient; STAT3, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; STAT5, signal transducer and activator of transcription 5; c-MYC; cellular myelocytomatosis; GLUT-1, glucose transporter 1; GLUT-3, glucose transporter 3; α-KG, alpha ketoglutarate; PKM2, pyruvate kinase M2; ENO-1, enolase-1; LDHα, lactate dehydrogenase-alpha; IDO, indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase; CSF-1,2, macrophage colony-stimulating factor 1, 2; c-TGF, connective-tissue growth factor; pDGF, platelet-derived growth factor; IGF-1, insulin-like growth factor 1; FGF, fibroblast growth factor; HGF, hepatocyte growth factor; EGF, epidermal growth factor; bFGF, basic insulin-like growth factor; G-CSF, granulocyte-colony stimulating factor; M-CSF, macrophage colony stimulating factor; MDSCs, myeloid-derived suppressor cells; T-regs, T regulatory cells; B-regs, B regulatory cells, CAFs, cancer associated fibroblast; EPCs, endothelial progenitor cells; MSCs, mesenchymal stem cells; TME, tumor microenvironment; ECM, extracellular matrix; AICD, antigen-mediated activation-induced cell death