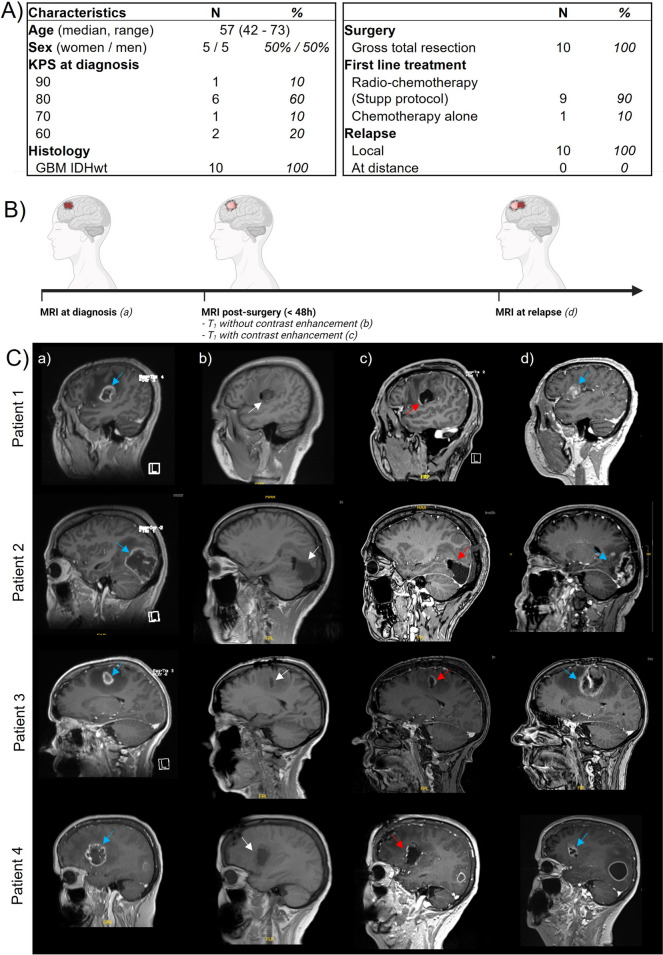
Fig. 3.
Surgery induces local modifications to the cerebral microenvironment in GBM patients. A) Patient characteristics of peri-operative cohort; B) Study design: GBM patients were enrolled in the study and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) was performed at time of diagnosis, within 48 h post-surgery (without and with contrast enhancement) and at relapse; C) Illustrative brain MRI imaging of four patients showing a T1 sequence with (a, c, d) or without (b) contrast enhancement, before (a) and after gross total resection (b and c) and at relapse (d). The blue arrows show the initial and recurrent tumor location, the white arrows show the tumor cavity location (b) and the red arrows show contrast enhancement associated with post-surgery BBB opening (c)