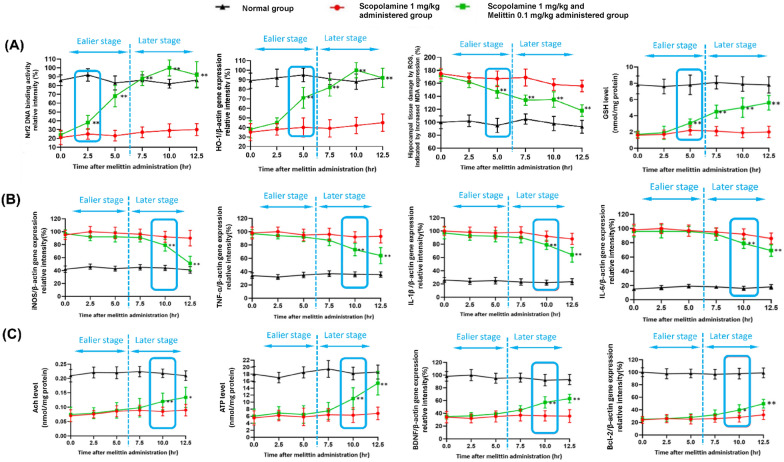
Fig. 7.
The findings suggest that the foremost notable impacts, happened in the earlier stage (0 to 5 h) after melittin administration were the restoration of Nrf2 DNA binding activity, leading to an increase in HO-1 gene expression to maintain cellular redox equilibrium; This first event was then subsequently followed by the rebalancing of inflammatory, apoptotic, cholinergic, and neurotrophic systems all happened in the later state (7.5 to 12.5 h). A Early activation and fortification of antioxidant mechanisms by Melittin: Within just 5 h of administration, a substantial elevation in Nrf2 DNA binding activity was observed. This subsequently triggered a pronounced rise in HO-1 gene expression, resulting in decreased levels of brain tissue MDA and enhanced GSH levels. (B) The expression of key inflammation regulators, including iNOS, TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β, was assessed. The results indicate that the stabilization of the inflammatory state did not become significant until the 10th hour. (C) Enhancement of acetylcholine neurotransmitters, brain ATP content, as well as Brain-derived neurotrophic factors BDNF and Bcl-2 anti-apoptosis gene expression, all exhibited no significant changes until the 10th hour (to the right of the blue dotted line); Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation. #p < 0.01 vs non-treatment group, * p < 0.01 compared with scopolamine only treated group; ** p < 0.001 compared with scopolamine only treated group; Five animals from each group were sacrificed at each time point for the analysis. Measurements were carried out triplicated, total animal tested n = 5/group