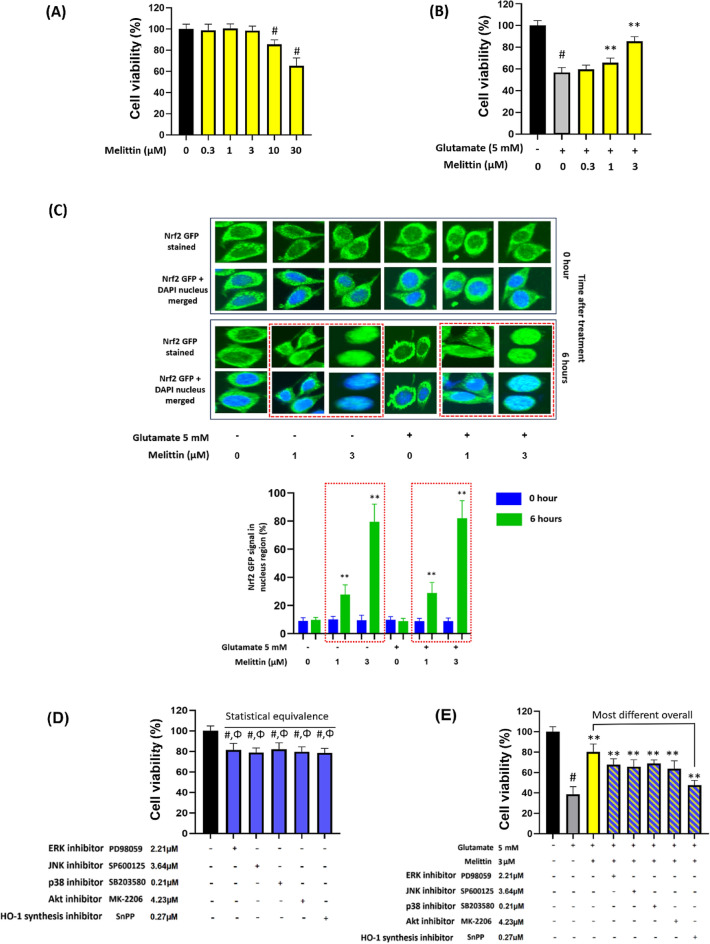
Fig. 8.
In vitro experiment with mouse hippocampal HT22 proposed that melittin directly engages with the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway to elicit a neuroprotective effect. A Screening for the optimal concentration of bee venom revealed that 3 μM melittin was the highest concentration that did not compromise HT22 cell viability 12 h after treatment. B Melittin exhibited a dose-dependent neuroprotective effect in the range of 0.3–3 μM against glutamate-induced stress, results measured 12 h after treatment. C Fluorescent staining revealed Nrf2 translocation into the nucleus following melittin treatment, with a significant nuclear Nrf2 signal at 1 and 3 μM concentrations. In the red-dotted squares, green, fluorescent Nrf2 signals overlap with the blue neuron nucleus. Higher melittin concentrations increase Nrf2 accumulation in the nucleus, indicating melittin promotes Nrf2 nuclear translocation in a concentration-dependent manner.4 D, E To elucidate the pathway most closely associated with melittin activity, various inhibitors targeting ERK, JNK, p38, Akt, and HO-1 synthesis were employed. D Inhibitor concentrations that inhibited approximately 80% of HT22 cell viability were identified. E Co-treatment of these concentrations with melittin and glutamate revealed that the HO-1 synthesis inhibitor exhibited the most pronounced reversal of melittin's positive effects. Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation. # p < 0.01 vs. non-treatment group; * p < 0.05 and ** p < 0.01 vs. glutamate only treatment group; p > 0.05 Statistical equivalence. Measurements were carried out triplicated