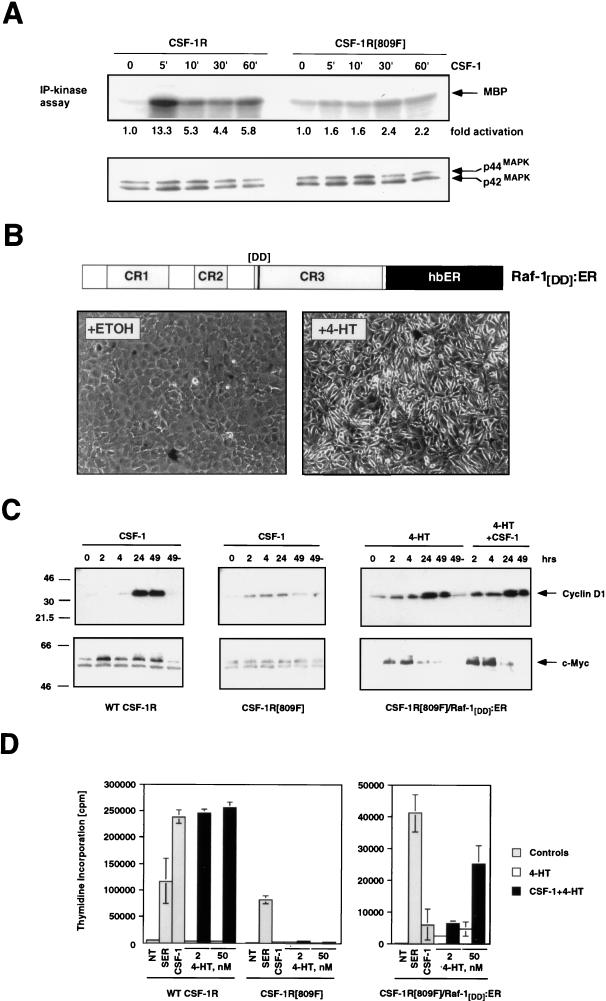
FIG. 4.
Complementation of the mitogenic and signaling defect of the CSF-1R[809F] by Raf. (A) Comparison of CSF-1-dependent MAP kinase activity in CSF-1R and CSF-1R[809F]-expressing cells. NIH 3T3 cells expressing either the wild-type human CSF-1 receptor (WT CSF-1R) or a mutated form of the receptor encoding a single tyrosine-to-phenylalanine mutation CSF-1R[809F] were cultured in DSFM for 24 h, at which time 300 nM CSF-1 was added for different periods of time as indicated. The activities of the p42 and p44 MAP kinases were measured by an immune complex kinase assay with MBP as a substrate, and the fold MAP kinase activation was quantified by PhosphorImager analysis (upper panel). Equal amounts of p42 and p44 MAP kinases in each immunoprecipitation were confirmed by Western blotting with an antiserum that recognizes p42 and p44 MAP kinases (lower panel). (B) Construction of a conditionally active form of full-length Raf-1. DNA sequences encoding a form of full-length human Raf-1 containing two activating point mutations (Y304D and Y341D) were fused in frame to sequences encoding the hormone-binding domain of the human estrogen receptor (hbER) to generate Raf-1[DD]:ER (diagram). NIH 3T3 cells infected with a replication-defective retrovirus encoding Raf-1[DD]:ER were treated with ethanol (solvent control) or 1 μM 4-HT for 48 h as indicated, at which time photomicrographs were taken. (C) Induced expression of c-Myc and cyclin D1. NIH 3T3 cells expressing either the wild-type CSF-1 receptor (left panel) or CSF-1R[809F] (middle panel) were cultured in DSFM for 40 h and treated with 300 nM CSF-1 for different periods of time as indicated. NIH 3T3 cells expressing both the CSF-1R[809F] and Raf-1[DD]:ER (right panel) were cultured in DSFM for 40 h, at which time they were treated with 50 nM 4-HT in the absence or presence of 300 nM CSF-1 for different periods of time as indicated. Expression of c-Myc and cyclin D1 was detected by Western blotting. For cyclin D1 detection, ECL exposures were all for the same length of time; for c-Myc, wild-type CSF-1R, and Raf-1[DD]:ER/CSF-1R[809F], Western blots were exposed for the same length of time but the CSF-1R[809F] Western blot was deliberately overexposed in order to detect the lower level of basal c-Myc expressed in these cells. (D) Proliferation of CSF-1R-expressing cell lines. NIH 3T3 cells expressing the wild-type CSF-1 receptor CSF-1R[809F] (left panel) or both CSF-1R[809F] and Raf-1[DD]:ER (right panel) were cultured in DSFM for 28 h and then either left untreated (NT) or treated with 10% FCS (SER), 300 nM CSF-1 (gray bars), 4-HT (2 or 50 nM, open bars), or CSF-1 plus 4-HT (solid bars). Cell proliferation was determined by measuring the incorporation of [3H]thymidine over a period of 36 h.