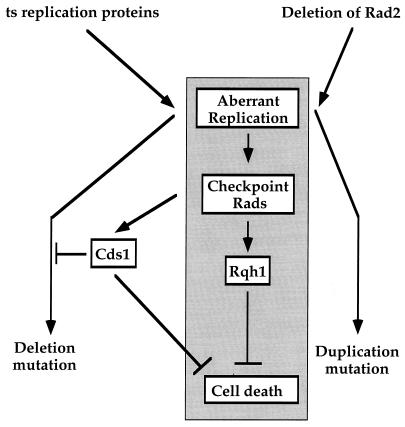
FIG. 3.
How checkpoint Rad proteins and Cds1 respond to aberrant replication in the deletion and duplication mutators. ts replication proteins at the semipermissive temperature and deletion of Rad2 generate different types of aberrant replication structures that are monitored by checkpoint Rad proteins. Checkpoint Rad proteins activate Rqh1 to prevent inappropriate recombination and cell death from both types of aberrant replication structures. In response to prevalent levels of aberrant replication specifically in ts replication mutators at the semipermissive temperature, checkpoint Rad proteins activate the Cds1-dependent recovery subpathway to prevent cell death and formation of deletion mutations. Some aberrant replication structures escape the Cds1-dependent recovery mechanism and thus result in deletion mutations. In the presence of lower levels of aberrant replication at the permissive temperature, Cds1 prevents formation of deletion mutations in the ts replication mutators. Details of these checkpoint responses are described in the Discussion.