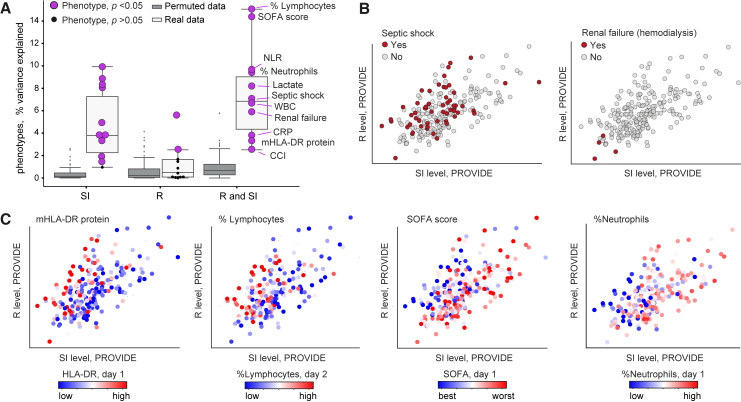
Figure 4.
The heterogeneity of clinical parameters within sepsis is associated with the impaired R/SI cell state
Data are shown for several physiological phenotypes across the PROVIDE clinical trial: SOFA scores in day 1 of hospitalization, quantity of the mHLA-DR protein in day 1 of hospitalization, the percentage of circulatory lymphocytes in day 2 of hospitalization, as well as septic shock, CCI, percentage of neutrophils, NLR, WBCs, lactate, CRP, and renal failure in day 1 of hospitalization.
(A) Boxplots for the percentages of inter-individual variance in phenotypes that are explained by either SI (left), R (middle), or the linear combination of R and SI (right), using either real (white) and permuted (gray) data. Each phenotype (a dot) is colored by purple/black for a significant/insignificant (empirical p < 0.05) percentage of explained variation.
(B and C) Scatterplots for SI and R levels (x and y axis, respectively) of each patient with sepsis (a dot), where each patient is colored by its level of a certain clinical parameter (indicated on top). The plots demonstrate the utility of the R and SI levels as biomarkers for the pathophysiology of sepsis. Related to Figure S5.