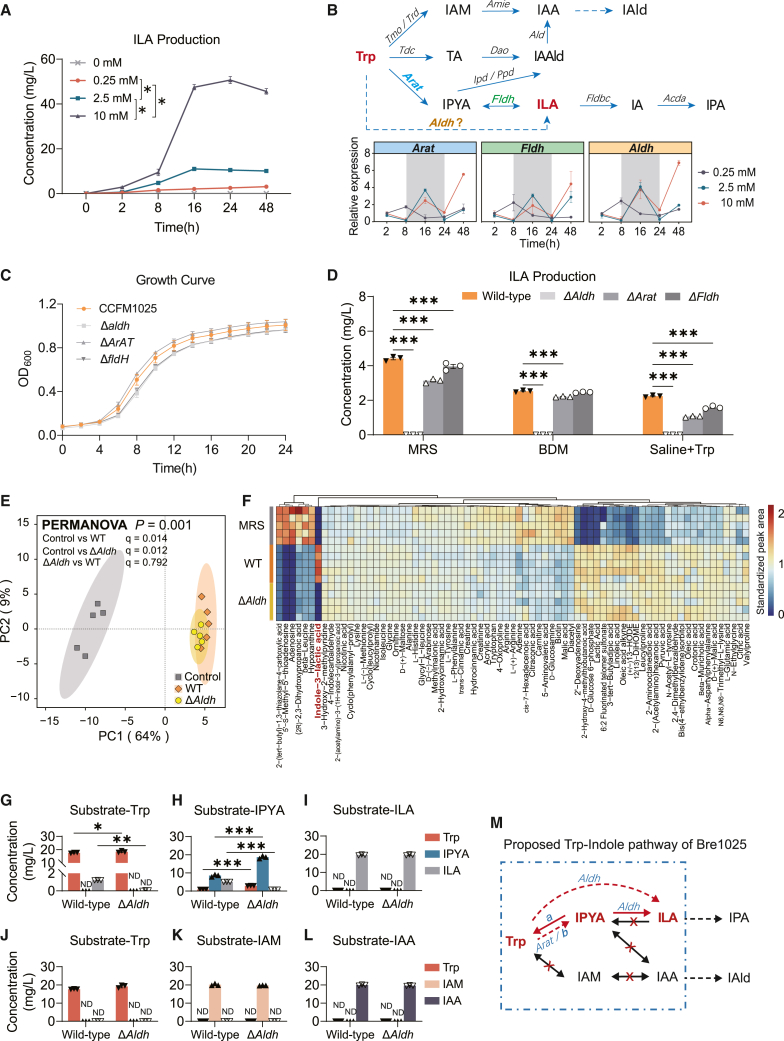
Figure 3.
Bre1025 metabolizes tryptophan to ILA through the Aldh gene
(A) ILA production by Bre1025 using tryptophan (Trp) as a substrate in a Bifidobacterium-defined medium (BDM) (n = 3/treatment).
(B) Expression of genes related to ILA production in Bre1025 with different amounts of Trp substrate. The upper pathway diagram depicts a schematic representation of how microorganisms metabolize Trp into indole derivatives. The bottom line chart displays the expression of genes in Bre1025 that are potentially involved in the microbial metabolism of Trp into ILA. IAM, indole-3-acetamide; IAA, indole-3-acetic acid; IAld, indole-3-aldehyde; TA, tryptamine; IAAld, indole-3-acetaldehyde; IPYA, indole-3-pyruvate; IA, indole acrylic acid; IPA, indole-3-propionic acid.
(C) In vitro growth curve of the Bre1025 mutant strain (n = 3/treatment). Wild-type: Bre1025 wild-type strain; Δtarget-gene: mutant strain of the Bre1025 target gene; ND, not detected.
(D) In vitro ILA production of the Bre1025 mutant strain.
(E) Principal component analysis illustrating the metabolome of the Bre1025 wild-type and mutant strains (n = 5/treatment). Control: mMRS medium supernatant.
(F) Metabolite heatmaps of Bre1025 wild-type and mutant strains (n = 3/treatment).
(G–L) Metabolism of Bre1025 in different substrates (n = 3/treatment).
(M) Proposed Trp-indole metabolism pathway of Bre1025.
∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, determined by two-tailed Student’s t test in (E–J) and one-way ANOVA followed by Sidak post hoc test in (A) and (D).