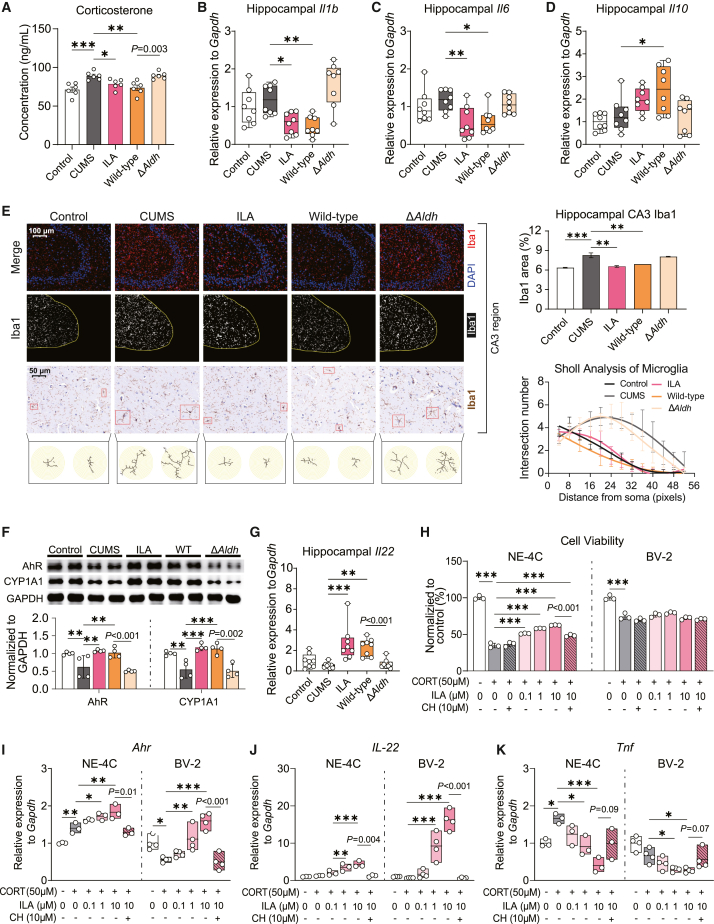
Figure 6.
Microbial-derived ILA alleviates neuroinflammation through the aryl hydrocarbon receptor
(A) Serum corticosterone concentrations in mice (n = 8/treatment).
(B–D) Expression analysis of genes associated with inflammatory factors in mouse hippocampus (n = 8/treatment).
(E) Immunofluorescence and immunohistochemical detection of Iba1 in the mouse brain (n = 3/treatment). Immunofluorescence analysis measured the percentage of Iba1 signal area relative to the total CA3 area in hippocampal. Sholl analysis was conducted on immunohistochemical slices to assess branching of labeled microglial cells, recording the intersection number every 4 pixels.
(F) Western blot analysis of aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) and CYP1A1 in the hippocampus of mice (n = 4/treatment).
(G) Expression of interleukin-22 gene (Il22) in mouse hippocampus (n = 8/treatment).
(H) Protective effect of ILA intervention on the viability of NE-4C and BV-2 cells (n = 3/treatment).
(I and J) Expression of AhR (Ahr) and IL-22 (Il22) in NE-4C and BV-2 cells (n = 3/treatment).
(K) Expression of TNF-α (Tnf) in NE-4C and BV-2 cells (n = 3/treatment).
∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, and ∗∗∗p < 0.001 indicate significant differences between groups, as determined by one-way ANOVA followed by Sidak post hoc test. P = numbers indicate significant differences between groups, as determined by two-tailed Student’s t test.