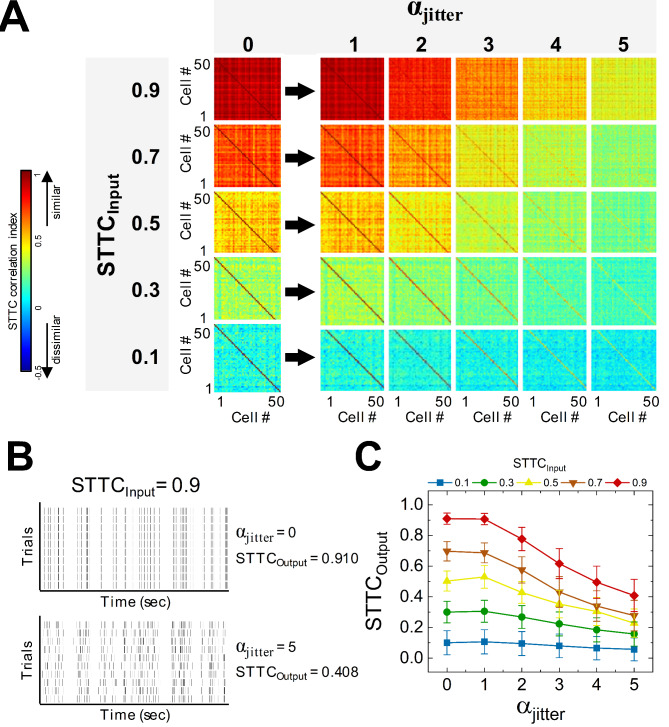
Fig. 5.
Heterogeneous spike trains are less affected by additional jitters than homogenous spike trains. (A) Color-coded matrices of spike time tiling coefficients (STTCs) visualize the level of pair-wise cross-correlation of spiking trains of 50 cells. STTC matrices were drawn before (αjitter = 0) and after adding jitters for αjitter ranging from 1 to 5. (B) Raster plots of spike trains representing ten trials without and with (upper and lower, respectively) jitters created by αjitter of 5 to original spike trains with STTCInput of 0.9. With no jitter, STTCOutput was 0.910 but STTCOutput became 0.408 by additional jitters. (C) Final STTC values (STTCsOutput) were plotted as a function of αjitter ranging from 0 to 5 for several input STTC values (STTCInput). Homogeneous spikes trains are more sensitive to the additional jitters in terms of final correlation levels.