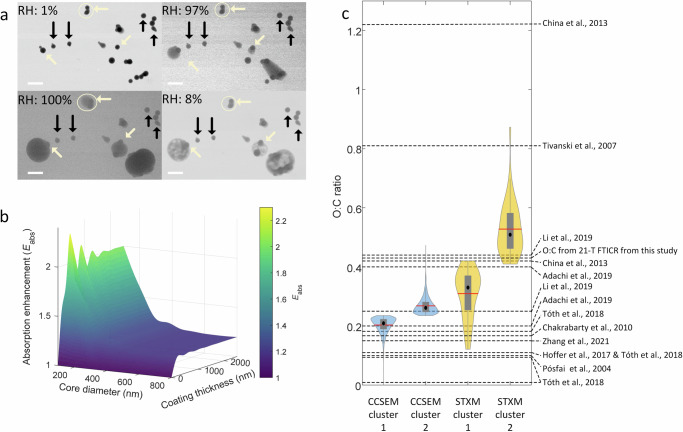
Fig. 4. Water uptake by solid S-BrC, lensing enhancement of solid S-BrC light absorption properties, and oxygen-to-carbon ratio for solid-state strongly absorptive brown carbon.
a Solid S-BrC water uptake experiment at 5 °C shows that some solid S-BrC did not uptake water (examples indicated by black arrows), and some are hydrophilic (examples indicated by light yellow arrows). Moreover, these solid S-BrC, which can uptake water, do not dissolve in water and form a water coating at high relative humidity (RH) conditions. The solid S-BrC selected by the light yellow cycles are solid S-BrC with thin organic coatings and can uptake water. The scale bar is 1 µm. b Lensing enhancement (Eabs) of solid S-BrC cores (diameters from 100 to 800 nm, RIsolid S-BrC,550 = 1.49 + 0.056i) coated with water (0–2500 nm thickness, RIwater,550 = 1.33 + 0i) at 550 nm (Eabs,water), which can vary between 1.004 and 2.851 (see Section S3). The Eabs is calculated as absorption cross-section (σabs) of the water-coated solid S-BrC particles (σabs,solid S-BrC,water) divided by σabs of the solid S-BrC cores (σabs, solid S-BrC). c O/C elemental ratio from this study and literature4,8,10,13,16,20,39,53,54. We also reference this study’s O:C ratio using 21-T FTICR MS data. The red lines indicate the means, the black dots are the medians, the gray rectangles are the interquartile ranges, the gray vertical lines are the 95% confidence intervals, and the violin-shaded areas show the data distribution.