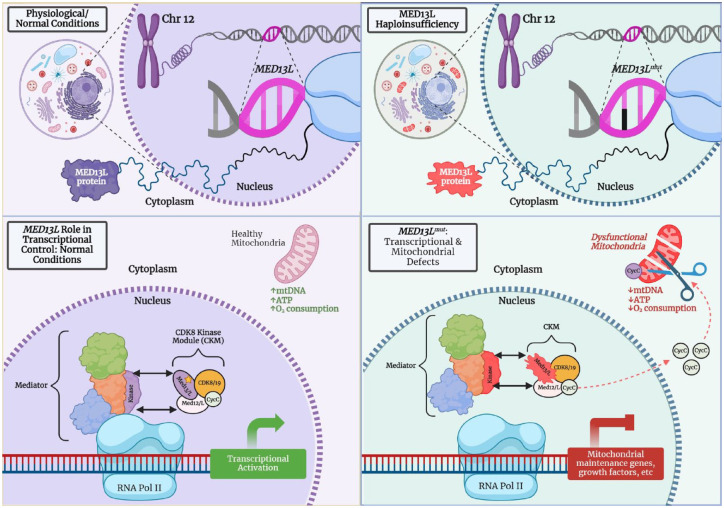
Figure 2.
Proposed mechanism of MED13L compared to MED13L haploinsufficiency (created with BioRender). Left side: Under normal conditions, one of the functions of MED13 is to link the MKM to the Mediator Complex46,47; presumably, MED13L has a similar function given that biochemical and mass spectrometry data show Mediator association with MED13 and MED13L.48,49 MED13L has specifically been shown to regulate Wnt, FGF, and Rb/E2F pathways.44,50,51 Additionally, upon induction of stress or a loss of the nuclear-tethering of MED13L, cyclin C has been shown to exit the nucleus and interact with mitochondrial fission machinery, promoting organelle fragmentation/fission.51–53 Right side: It is hypothesized that in MED13L Haploinsufficiency Syndrome, the transcriptional process related to the mediator complex interaction with RNA polymerase II may be disrupted. Cyclin C is aberrantly released into the cytoplasm, increasing susceptibility to cell death through mitochondrial fragmentation, decreased oxygen consumption as well as decreased ATP production.50,53
FGF, fibroblast growth factor; MKM, mediator kinase module; Rb/E2F, retinoblastoma tumor suppressor; Wnt, wingless-type integration type.