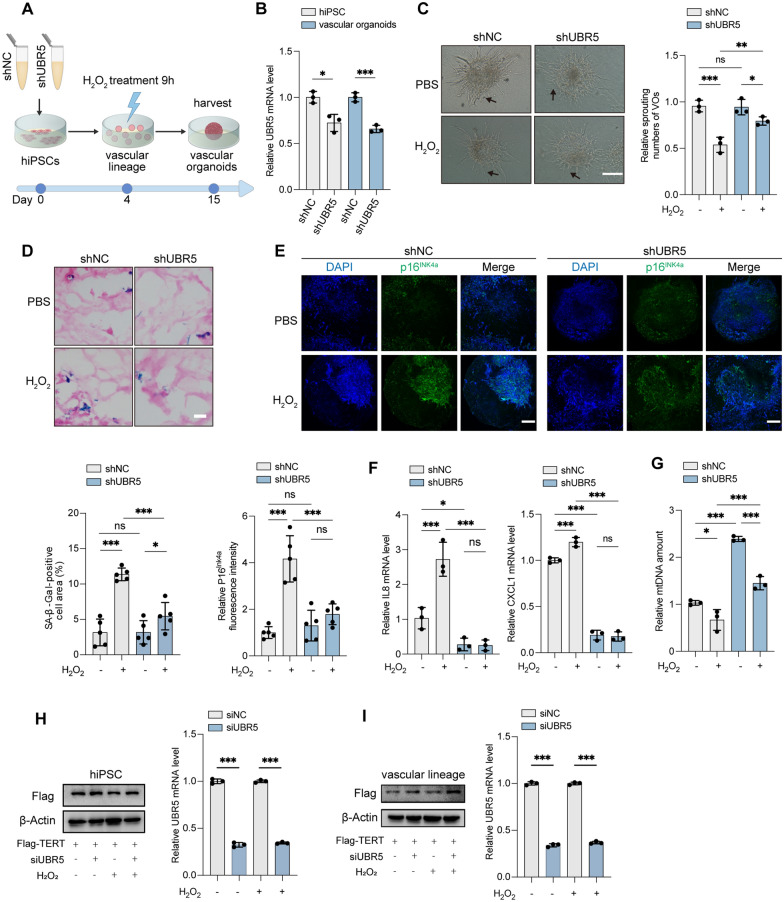
Fig. 5.
Inhibition of UBR5 alleviates ROS-induced VO impairment. A Schematic timeline of H2O2 treatment of VOs. hiPSCs expressing shNC or shUBR5 were subjected to 50 μM H2O2 or PBS for 9 h at the vascular lineage stage (day 4). B Relative UBR5 mRNA levels in hiPSCs and VOs were assessed by RT-qPCR. C VOs were imaged after treatment with 50 μM H2O2 or PBS for 9 h at the vascular lineage stage (day 10). Arrows indicate neovascular sprouting. Scale bars: 300 μm. Sprouting numbers were quantified using ImageJ. D SA-β-Gal staining of VOs at day 15. Scale bars: 50 μm. The percentage of SA-β-Gal-positive cell area (blue) relative to eosin-stained area (red) was quantified. The values were obtained from five randomly selected fields. E IF staining of VOs for p16INK4a (green) to mark senescent cells, with DAPI (blue) for nuclei. Scale bars: 250 μm. p16INK4a fluorescence intensity was quantified from five randomly chosen fields. F Relative SASP (IL8, CXCL1) levels in VOs determined by RT-qPCR. G Relative mtDNA levels in VOs determined by RT-qPCR. H-I hiPSC-Flag-TERT cells were transiently transfected with siNC or siUBR5, followed by treatment with 50 μM H2O2 or PBS. H Western blot analysis showing Flag levels in lysates from hiPSC-Flag-TERT (left). Relative UBR5 mRNA levels were assessed by RT-qPCR (right). I Western blot analysis showing Flag levels in lysates from vascular lineage developed from hiPSC-Flag-TERT (left). Relative UBR5 mRNA levels were assessed by RT-qPCR (right). (ns, not significant; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001)