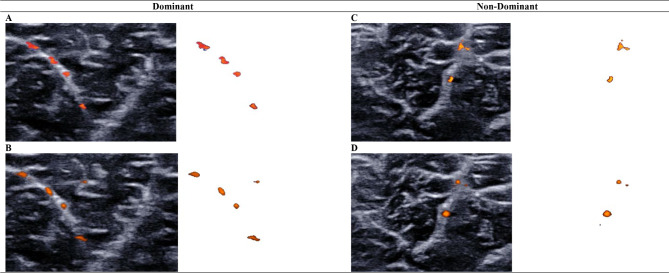
Fig. 2.
Comparing medial gastrocnemius intramuscular blood perfusion between imaging techniques using the vascularity index
Intramuscular blood perfusion of the medial gastrocnemius muscle was measured with color Doppler flow imaging (A, C) and Angio PLanewave UltraSensitive Imaging (B, D). Isolated color pixels were used to calculate the vascularity index for dominant (A, B) and non-dominant (C, D) medial gastrocnemius muscles. Color Doppler flow imaging and Angio PLanewave UltraSensitive Imaging demonstrated similar sensitivity in detecting intramuscular blood flow of the medial gastrocnemius muscle