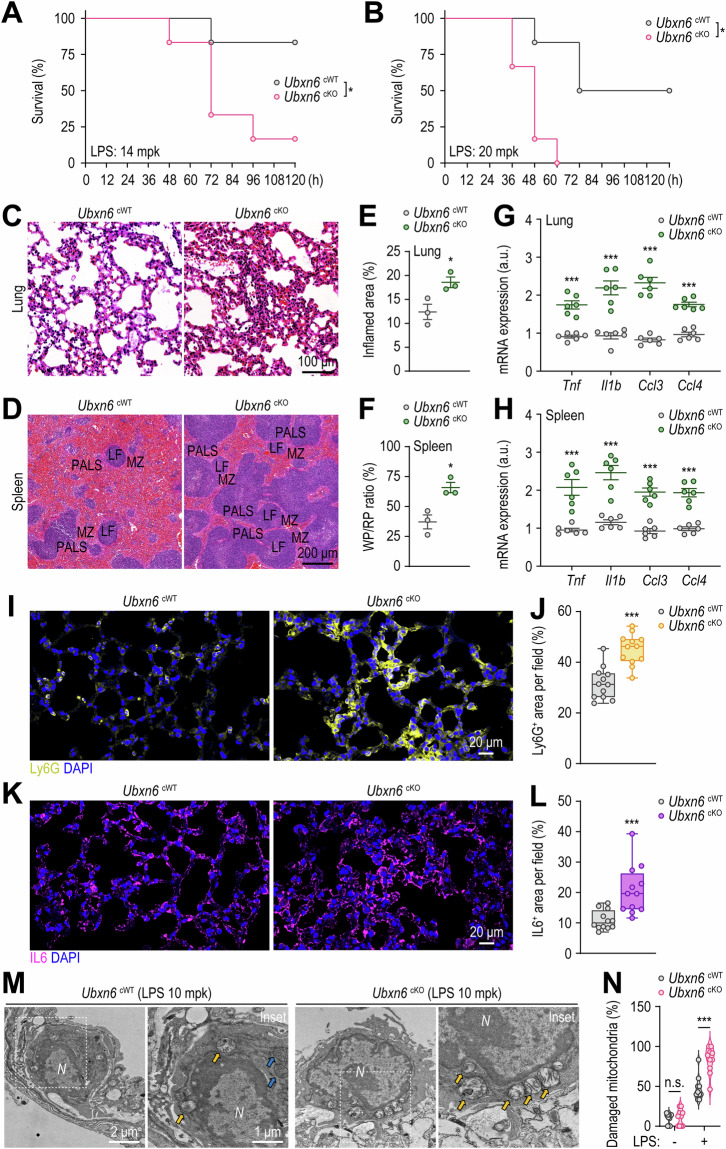
Fig. 7.
UBXN6 attenuates sepsis-induced mortality and systemic inflammation in vivo. A, B Survival of Ubxn6 cWT and cKO mice assessed for 120 h after the administration of LPS (14 mg/kg, n = 6) (A) or LPS (20 mg/kg, n = 6) (B). C–F Hematoxylin and eosin-stained sections of lungs (C) and spleen tissues (D), with relative quantification of inflamed areas in the lungs (E) and the red-to-white pulp ratio in the spleens (F) of mice challenged with LPS (14 mg/kg) for 24 h. G, H Relative mRNA levels of Tnf, Il1b, Ccl3, and Ccl4 in the lungs (G) and spleens (H) of mice injected with LPS (14 mg/kg) for 6 h. I–L Representative confocal microscopy images of Ly6G (I)- and IL6 (K)-stained cells, with positive areas per field quantified for Ly6G (J) and IL6 (L), respectively. Paraffin sections of lung tissues from the mice used in (C) were immunostained with Ly6G (yellow), IL6 (purple), and DAPI (blue for nuclei). M, N TEM images (M) and quantification of damaged mitochondria (N) from alveolar macrophages in ALI model mouse lung tissues. The mice were treated with or without LPS (10 mg/kg) for 24 h before their lungs were analyzed via TEM. The yellow or blue arrows indicate swollen or intact mitochondria, respectively. Statistical significance was determined via either the log-rank (Mantel‒Cox) test (A, B) or two-tailed Student’s t test (E–H, J, L, and N). PALS, periarteriolar lymphoid sheaths; LF, lymphoid follicle; MZ, marginal zone; WP, white pulp; RP, red pulp; a.u., arbitrary unit; N, nuclei; n.s., not significant. The data represent the means ± SEM from 3‒6 biological replicates (E–N). *p < 0.05 and ***p < 0.001