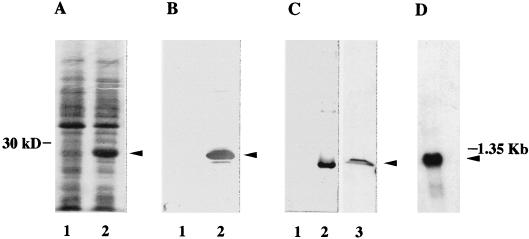
FIG. 1.
Analysis of the protein and the mRNA encoded by the TIF6 gene. (A) Expression of yeast eIF6 in E. coli. Cell extracts, prepared from IPTG-induced cultures of E. coli BL21(DE3) cells harboring either the parental plasmid pET-5a (lane 1) or pET-TIF6 (lane 2), were electrophoresed in an SDS–15% polyacrylamide gel and subjected to Coomassie blue staining. The position of migration of the expressed protein of about 26 kDa is shown by an arrowhead. (B) Immunoblot analysis of the bacterially expressed 26-kDa protein with mammalian anti-eIF6 antibodies as probes. Cell extracts of IPTG-induced cultures of BL21(DE3) cells harboring either the parental vector (lane 1) or the pET-TIF6 recombinant expression plasmid (lane 2) were subjected to Western blot analysis with monospecific anti-mammalian eIF6 antibodies (32) as probes. (C) Immunoblot analysis with anti-TIF6p (eIF6) antibodies as probes. The protein samples used in lanes 1 and 2 were the same as those used in lanes 1 and 2 of panel B, while lane 3 contained 100 μg of a partially fractionated protein fraction derived from cell extracts of S. cerevisiae W303 (a/α). Immunoblot analysis was carried out with anti-yeast 26-kDa Tif6p antibodies as probes. A set of molecular weight marker proteins was run in a separate lane of each gel (data not shown). The position of eIF6 is shown by an arrowhead. (D) Northern blot analysis of mRNA expressed from the TIF6 gene. A Northern blot containing 2 μg of electrophoretically separated yeast poly(A)+ RNA was hybridized to a 32P-labeled 735-bp TIF6 ORF. The blot also contained a set of RNA size markers, of which the position of 1.35-kb RNA is indicated. The blot was analyzed by autoradiography.