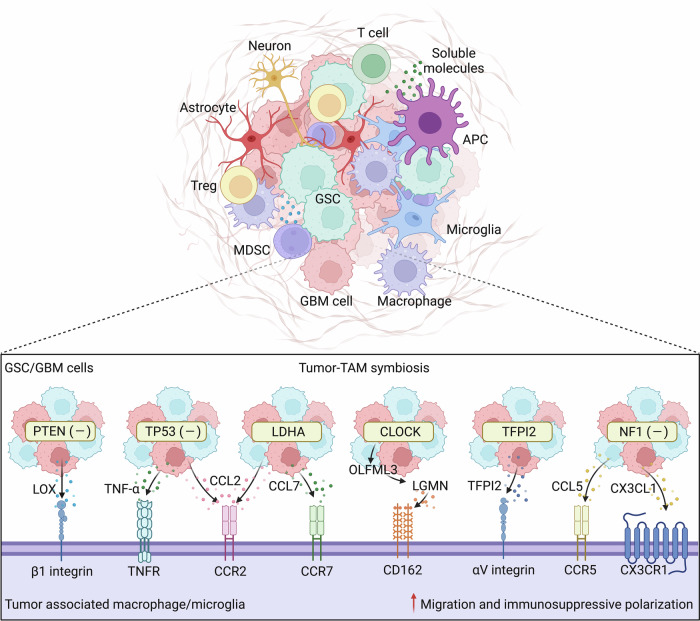
Fig. 3.
The immunosuppressive TME and tumor-TAM crosstalk in GBM. The immunosuppressive TME of GBM is a highly heterogeneous dynamic system that includes tumor cells (GBM cells and GSCs), low numbers of TILs, high infiltration of immunosuppressive cells (e.g., TAMs, MDSCs, and Tregs), normal brain cells (e.g., astrocytes and neurons), and soluble molecules. Crosstalk between tumor cells and TAMs is an important mechanism within the GBM TME that promotes tumor growth and induces immunosuppression. Under different conditions (e.g., PTEN, P53 and NF1 deletion/mutation, CLOCK and TFPI2 overexpression/amplification, and metabolic changes), tumor cells can secrete various cytokines and chemokines, such as LOX, TNF-α, OLFML3, LGMN, TFPI2, CCL2, CCL5, CCL7, and CX3CL1, to promote the migration and immunosuppressive polarization of TAMs, which in turn promotes tumor progression and immunosuppression. APCs antigen-presenting cells, CCL2 C-C motif chemokine ligand 2, CD162 cluster of differentiation 162, CLOCK circadian locomotor output cycles kaput, CX3CL1 C-X3-C motif ligand 1, CX3CR1 C-X3-C motif chemokine receptor 1, GBM glioblastoma, GSCs glioblastoma stem cells, LDHA lactate dehydrogenase A, LOX lysyl oxidase, LGMN legumain, MDSCs myeloid-derived suppressor cells, NF1 neurofibromin 1, OLFML3 olfactomedin like 3, TAMs tumor-associated macrophages and microglia, TFPI2 tissue factor pathway inhibitor 2, TILs tumor infiltrating lymphocytes, TME tumor microenvironment, TNF-α tumor necrosis factor α, TNFR, CCR2 C-C motif chemokine receptor 2, TNFR TNF-α receptor, Tregs regulatory T cells