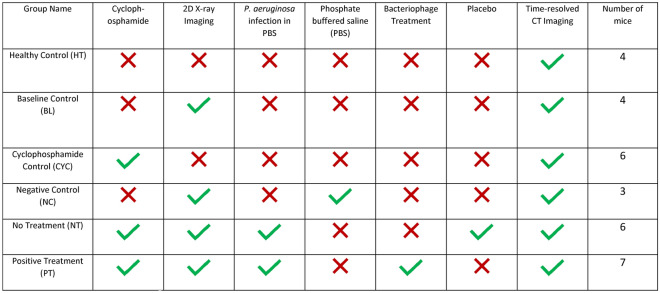
Table 1.
Mouse groups and the associated interventions.
Cyclophosphamide (Baxter Healthcare Pty Ltd., New South Wales, Australia) was administered to the relevant mice via intraperitoneal injection, with a 150 mg/kg dose given four days prior to imaging and a 100 mg/kg dose given one day prior to imaging. An initial 2D X-ray was taken prior to infecting the mice with P. aeruginosa (or phosphate buffered saline (PBS) sham in the case of group NC). There was a minimal delay of less than ten minutes between the initial imaging and the infection delivery. An inoculum was prepared with P. aeruginosa in PBS, and a 25μL dose was delivered to the lung of the anaesthetised animals using intra-tracheal instillation. Where appropriate, the bacteriophage powder treatment was administered intratracheally, under anaesthesia, at two hours post infection. In the case of the No Treatment group, a puff of the same volume of air was delivered at this timepoint as a placebo. The mice were then left to recover for 24 h before the final imaging with both time-resolved CT and 2D X-ray.