Fig. 8. Ultrafast ophthalmic AO converges faster during sequential fixation.
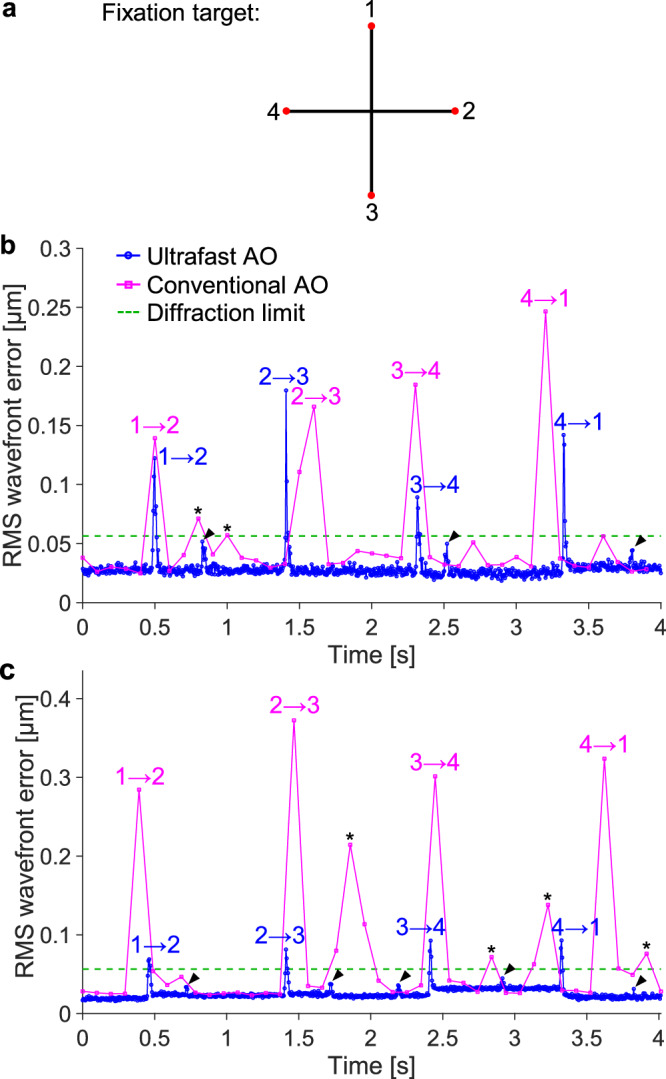
a Subject sequentially fixated for one second at each of the four corners of a cross on a display, moving fixation after an audible beep sounded every second. b RMS wavefront error over time for the subject with the median aberration power spectrum among the five subjects measured. Numeric labels, i → j, denote the time immediately after the subject changed his fixation from location i to j. Arrowhead and asterisk symbols denote the wavefront error spikes with ultrafast AO and the wavefront error spikes that are above the diffraction limit with conventional AO, respectively, before the subject changed his fixation to the next location. c RMS wavefront error over time for the subject with the largest aberration power spectrum among the five subjects measured. This subject is the oldest of the five and has 2× larger higher-order aberrations as measured with a clinical aberrometer (Pentacam AXL Wave, Oculus).
