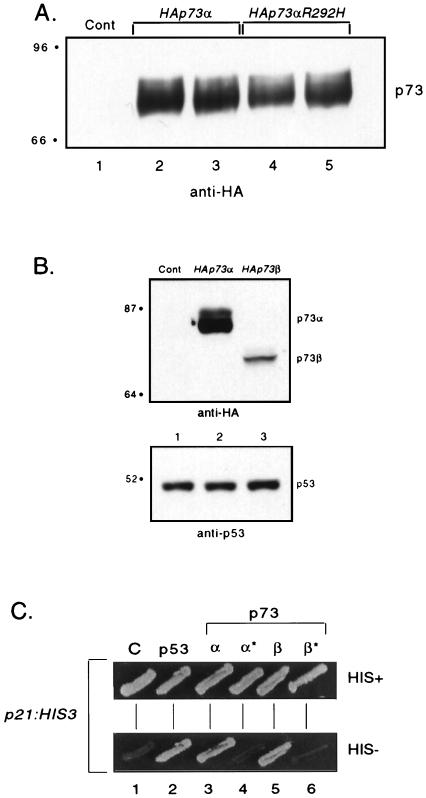
FIG. 3.
Expression levels of p73 in yeast. (A) Wild-type- and mutant p73α-expressing strains were grown to log phase; extracts were prepared and subjected to Western blot analysis in which 50 μg of total cell extract was loaded. The Western blot was probed with an anti-HA antibody at a 1/3,000 dilution. Shown is the expression from two independently isolated wild-type and mutant p73α clones. “Cont” (lane 1) refers to a strain containing a control vector (ADH1 promoter on a LEU2/2μm plasmid). (B) Wild-type p73α- and p73β-expressing strains were grown to log phase; extracts were prepared and subjected to Western blot analysis in which 100 μg of total cell extract was loaded. The Western blot was probed with an anti-HA antibody at a 1/3,000 dilution (top) and a mixture of anti-p53 antibodies at a 1/3,000 dilution (bottom). These strains also express wild-type untagged p53, which was used as a loading control. “Cont” (lane 1) refers to a strain containing a control vector (ADH1 promoter on a LEU2/2μm plasmid) and wild-type p53 (ADH1 promoter p53 on a URA3/CEN vector). (C) Strains expressing wild-type p53, p73α, or p73β, or mutant p73α or p73β, and containing a p53-responsive reporter (p21:HIS3 on a TRP/CEN plasmid) were patched onto SC-minus-leucine-minus-tryptophan plates and grown for 1 day at 37°C. Patches were replica plated onto SC-minus-leucine-minus-tryptophan-minus-histidine plates and grown for 1.5 days at 37°C. *, mutant p73αR292H or p73βR292H; C, strain containing a control vector (ADH1 promoter on a LEU2/CEN plasmid). Sizes in panels A and B are indicated in kilodaltons on the left.