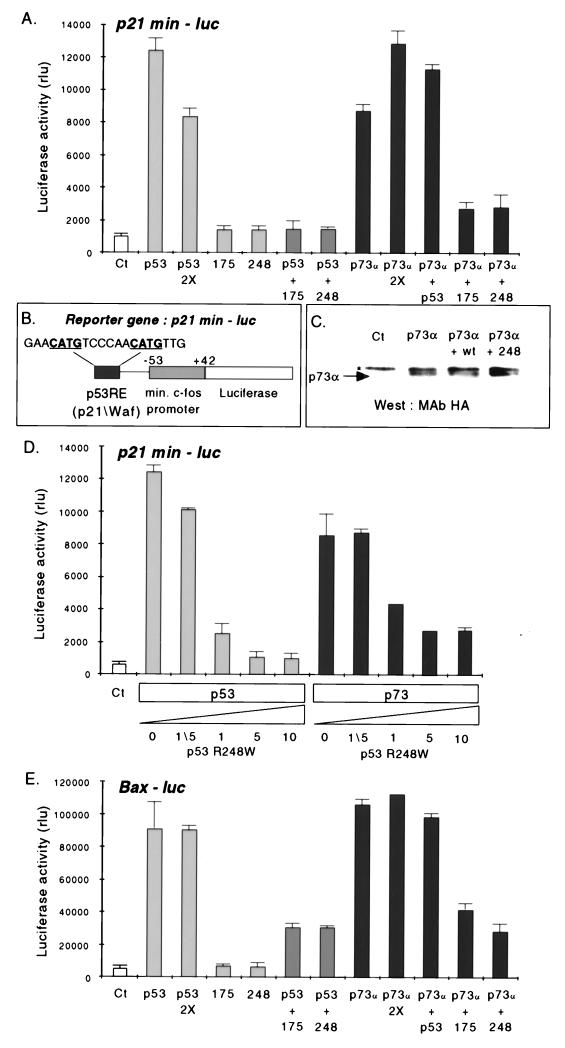
FIG. 5.
Tumor-derived p53 mutants reduce the transcriptional activity of p73α. (A) H1299 cells were transiently cotransfected with a reporter plasmid (p21min-luc) containing a derived p53-responsive human target gene cis-acting element from the p21 promoter (see panel B and Materials and Methods), and a plasmid expressing either p73α, wild-type p53 (p53), p53R175H (175), or p53R248W (248). In each transfection, equivalent amounts of DNA were used for all expression plasmids except where indicated (“2×” refers to a twofold increase in the amount of expression plasmid DNA transfected). (C) Representative Western blot loaded with 100 μg of extract and probed with anti-HA antibody 12CA5 to detect p73α in cells expressing either p73α alone, p73α plus wild-type p53 (wt), or p73α plus p53R248W (248). Ct, control plasmid; ∗, a nonspecific protein band that migrates more slowly than p73α and cross-reacts with the anti-HA antibody. (D) H1299 cells were cotransfected with increasing amounts of the p53R248W expression plasmid and a constant amount of either wild-type p53 or p73α and the p21min-luc reporter as for panel B. Ct, control plasmid; 0, 1/5, 1, 5, and 10, fold excess of p53R248W DNA used in the cotransfection. (E) H1299 cells were cotransfected as described for panel A except that the luciferase reporter construct used (Bax-luc) contained the full length Bax promoter. For the luciferase assays in panels A, D, and E, histograms represent relative luciferase units (rlu) and diagrams show the mean of a typical experiment of three performed in triplicate (bars indicate standard deviations).