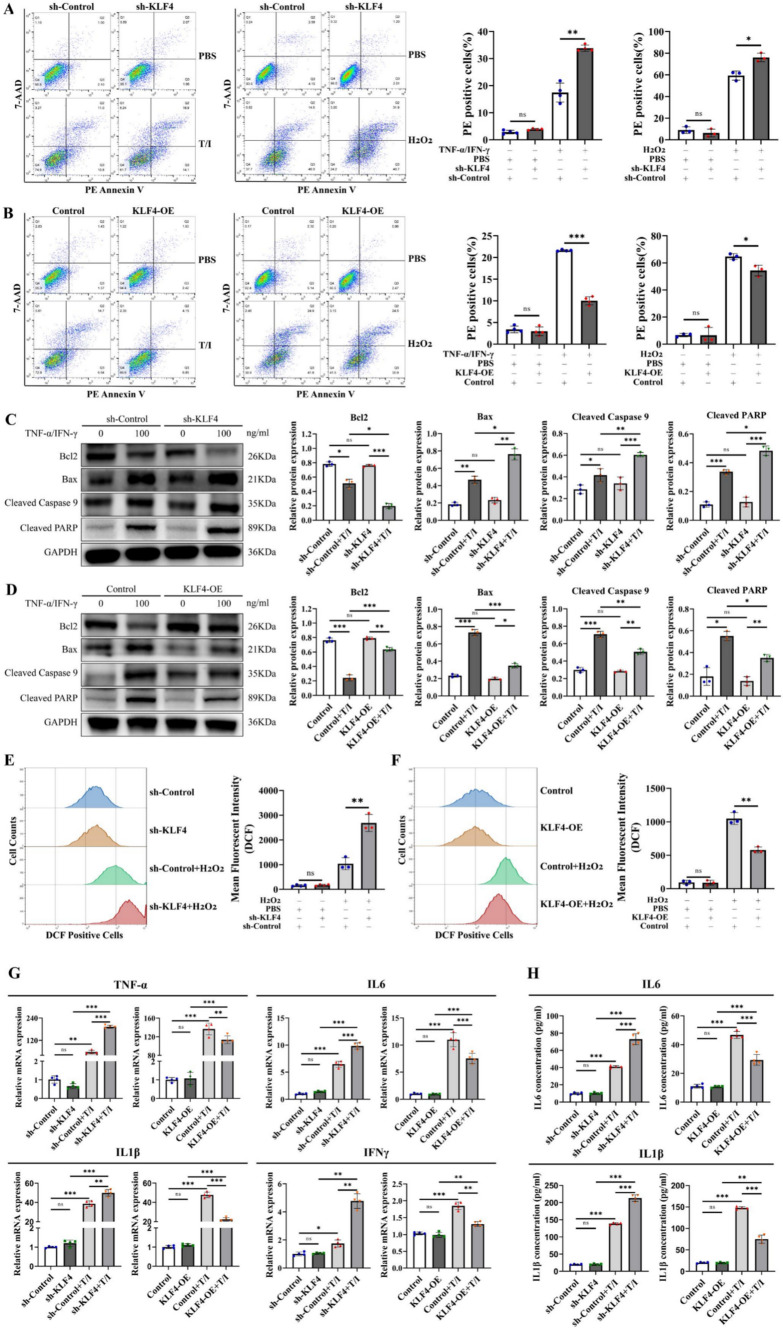
Fig. 5.
KLF4 knockdown increases intestinal epithelial cell apoptosis by increasing cellular ROS and proinflammatory cytokine levels. A, B Apoptotic cells were detected using Annexin V/7-AAD double staining in KLF4-knockdown (A) or KLF4-overexpressing (B) Caco-2 cells after treatment with H2O2 (10 μmol/L) or TNF-α/IFN-γ (100 ng/mL). C, D The protein expression of Bcl2, Bax, cleaved caspase-9 and cleaved PARP in KLF4-knockdown (C) and KLF4-overexpressing (D) Caco-2 cells stimulated with TNF-α/IFN-γ (100 ng/mL). The Western blot band densities shown in (C, D) were quantified using ImageJ software. E, F The levels of intracellular ROS in KLF4-knockdown (E) or KLF4-overexpressing (F) Caco-2 cells treated with H2O2 (10 μmol/L) were determined using a DCFH-DA probe and flow cytometry. G The mRNA expression of TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β and IFNγ in KLF4-knockdown or KLF4-overexpressing Caco-2 cells stimulated with TNF-α/IFN-γ (100 ng/ml). H The IL1β and IL-6 concentrations in the cell supernatant of KLF4-knockdown or KLF4-overexpressing Caco-2 cells stimulated with TNF-α/IFN-γ (100 ng/ml) were detected using ELISA. The data are expressed as the mean ± SD. ns, not significant, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001