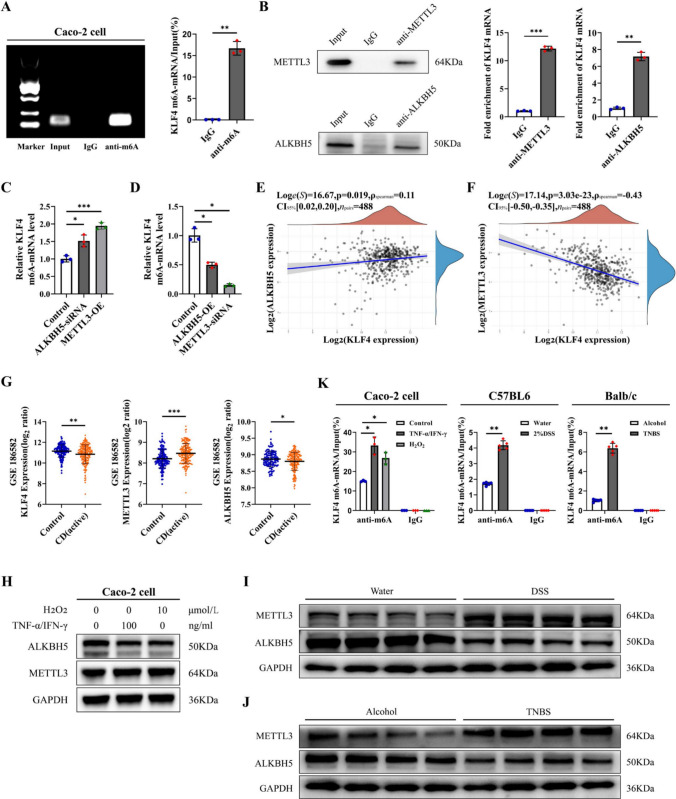
Fig. 6.
METTL3 and ALKBH5 mediated the m6A modification of KLF4. A MeRIP-PCR analysis of m6A enrichment on the mRNA of KLF4. B RIP-qPCR analysis showed that the ALKBH5 protein and METTL3 protein bind to KLF4 mRNA. C Depletion of ALKBH5 and overexpression of METTL3 elevated m6A levels on KLF4 mRNA in Caco-2 cells. D Overexpression of ALKBH5 and knockdown of METTL3 reduced m6A levels on KLF4 mRNA in Caco-2 cells. E Spearman’s correlation between KLF4 and ALKBH5 expression in the GSE186582 dataset (n = 488). F Spearman’s correlation between KLF4 and METTL3 expression in the GSE186582 dataset (n = 488). G Transcript levels of METTL3, ALKBH5, and KLF4 in control (n = 147) and CD patient (n = 196) samples from the GSE186582 dataset. H The protein expression of METTL3 and ALKBH5 in Caco-2 cells after H2O2 (10 μmol/L) or TNF-α/IFN-γ (100 ng/ml) stimulation was detected by Western blot. I, J The protein expression of METTL3 and ALKBH5 in the colon tissues of DSS-induced (I) and TNBS-induced (J) colitis model mice. K m6A modification of KLF4 mRNA in Caco-2 cells after H2O2 (10 μmol/L) or TNF-α/IFN-γ (100 ng/ml) stimulation (left), DSS-induced colitis (middle) or TNBS-induced colitis (right). The data are expressed as the mean ± SD. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001