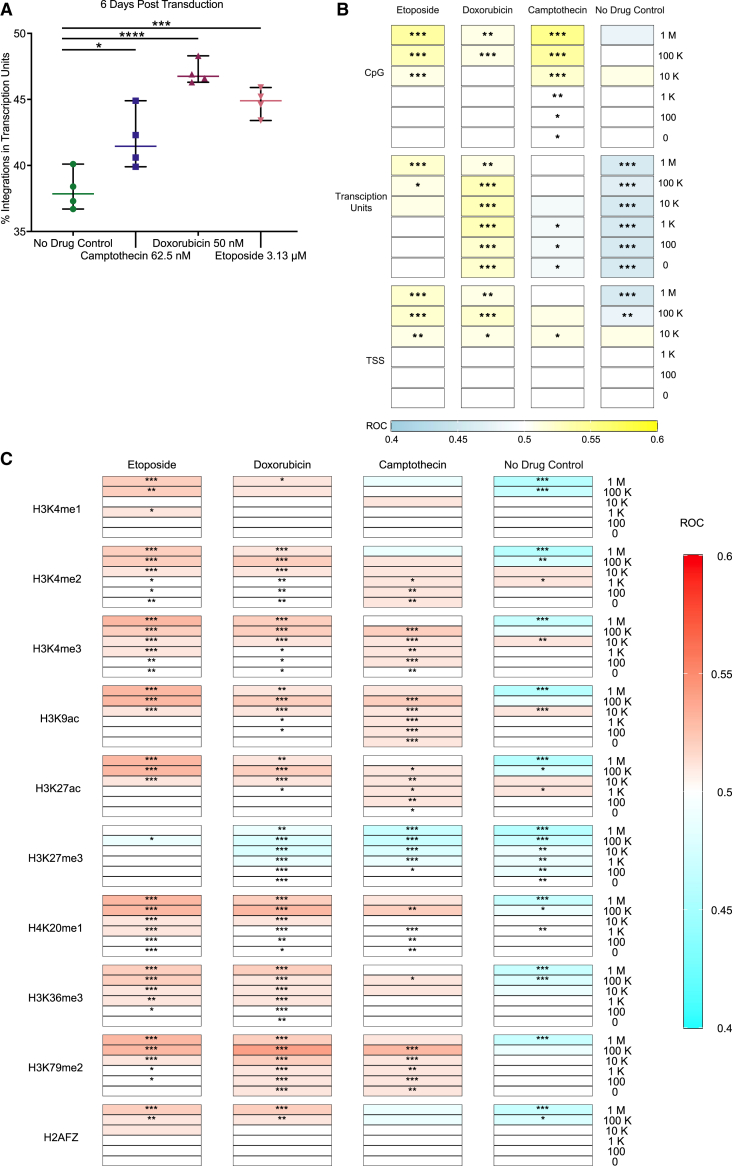
Figure 5.
CPT-, DOX-, and ETO-treated HeLa cells have different patterns of AAV integration relative to genomic features
(A) The percentage of integration sites in transcription units was calculated for each biological replicate. Data displayed are the values for each biological replicate (n = 4) with the mean displayed as a horizontal bar. Medium only (no drug control, green circles), 62.5 nM of CPT (blue squares), 50 nM DOX (maroon upward triangles), or 3.13 μM of ETO (pink downward triangles). Data were analyzed using one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparison test of each drug against the control cells. ns, no significance; ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001. (B and C) Distribution of the AAV vector integration sites in the human genome relative to random controls (three times the number of sites as each experimental measure). Tracks are grouped by (B) genomic features or (C) histone markers/chromatin features. All biological replicates are collapsed by treatment condition, and associations were calculated versus random distributions using the ROC area method.35 Values of the ROC were scaled between 0.4 (negatively associated, (B) blue or (C) aqua) and 0.6 (positively associated, (B) yellow or (C) red). Significance was calculated by the ROC method (∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001).