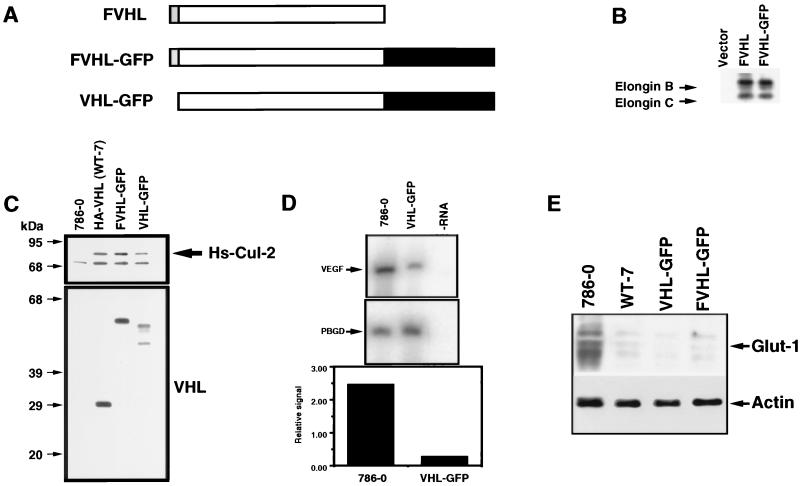
FIG. 1.
Functional comparison of wild-type VHL and VHL linked to the GFP. (A) Schematic diagram of VHL fusion to the GFP. The VHL cDNA codes for a 213-amino-acid protein (open box). A Flag-tagged epitope (F) was fused at the N-terminus (shaded box). The GFP was fused at the C terminus (black box [not in scale]), resulting in FVHL-GFP. A version without the Flag tag was also produced (VHL-GFP). (B) FVHL-GFP assembles with elongins B and C. Cos-7 cells were transfected with 5 μg of plasmid DNA, plated for 16 h, incubated for 6 h in the presence of [35S]Met, and immunoprecipitated with the M2 anti-Flag antibody as described in Materials and Methods. Vector, pSX. (C) FVHL-GFP and VHL-GFP assemble with Hs-Cul-2. Stable VHL-negative RCC 786-0 cells (786-0) expressing either HA-tagged VHL (WT-7), Flag-tagged VHL-GFP to force expression from the first methionine of VHL (FVHL-GFP), or a GFP fusion without the Flag tag (VHL-GFP) to produce fusion proteins initiated by two methionines were lysed and immunoprecipitated with a monoclonal anti-VHL antibody. Precipitated proteins were run on SDS-PAGE (12% polyacrylamide) and transferred on a nitrocellulose membrane. The membrane was incubated in the presence of rabbit anti-Hs-Cul-2 (top panel) or rabbit anti-VHL (bottom panel) antibodies. Notice that FVHL-GFP and VHL-GFP assemble with Hs-Cul-2, as does HA-VHL (WT-7) (an arrow points at Hs-Cul-2). FVHL-GFP produces a single protein with a size of approximately 55 kDa, whereas VHL-GFP produces two proteins presumably initiated from two methionines, a phenomenon sometimes observed with endogenous VHL and a VHL cDNA with an epitope tagged at the C terminus (9). (D) VHL-GFP inhibits the production of VEGF mRNA. RT-PCR was performed as described in Materials and Methods with primers specific for VEGF mRNA and PBGD mRNA as a control. Also shown is a quantification of the VEGF/PBGD signal ratios. −RNA, RT-PCR was performed in buffer without RNA. (E) FVHL-GFP and VHL-GFP downregulate levels of Glut-1 protein. Total cell extracts obtained from 786-0, WT-7 (expressing HA-VHL), FVHL-GFP, and VHL-GFP were run on SDS-PAGE (10% polyacrylamide) gel and transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane, and the membrane was incubated in the presence of an anti-Glut-1 antibody. Notice the high levels of Glut-1 in 786-0 cell extract and that FVHL-GFP and VHL-GFP downregulate Glut-1 levels, as does HA-VHL (WT-7). Blots were also incubated with actin as a loading control.