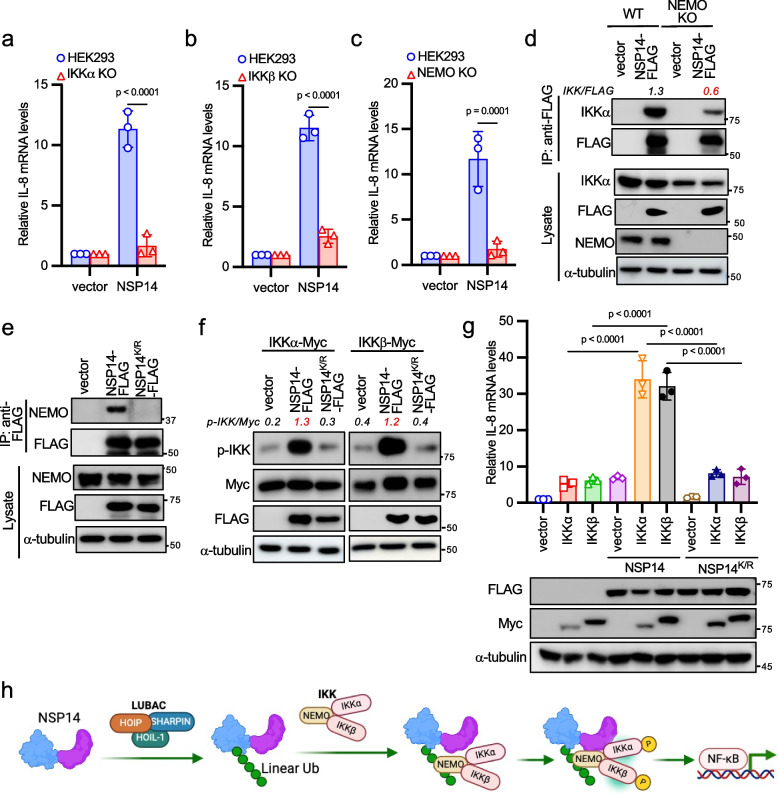
Fig. 5.
NSP14-mediated NF-κB activation through the IKK complex. a-c Transfection of either vector or NSP14-FLAG into wild-type, IKKα knockout (a), IKKβ knockout (b), or NEMO knockout (c) HEK293 cells for 24 h. Real-time PCR analysis was conducted to determine the relative IL-8 mRNA levels. d Vector or NSP14-FLAG was transfected into NEMO wild-type and knockout HEK293 cells. After 48 h, cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with the anti-FLAG antibody and blotted with anti-FLAG, anti-IKKα, anti-NEMO, and anti-α-tubulin antibodies. e Vector, NSP14-FLAG, or NSP14K/R-FLAG was transfected into HEK293 cells. After 48 h, cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with the anti-FLAG antibody and blotted with anti-FLAG, anti-NEMO, and anti-α-tubulin antibodies. f NSP14-FLAG or NSP14K/R-FLAG was transfected with Myc-tagged IKKα or IKKβ into HEK293 cells. After 48 h, cell lysates were blotted with anti-FLAG, anti-Myc, anti-p-IKK (Ser176/180), and anti-α-tubulin antibodies. g FLAG-tagged NSP14 or NSP14K/R was transfected with Myc-tagged IKKα or IKKβ into HEK293 cells for 24 h. Real-time PCR analysis was performed to determine the relative IL-8 mRNA levels. Lysates were blotted with anti-FLAG, anti-Myc, and anti-α-tubulin antibodies. The p-value was calculated by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's multiple comparisons test (g) or two-way ANOVA followed by Sidak's multiple comparisons test (a, b, c). h Model illustrating NSP14 linear polyubiquitin-mediated NEMO recruitment and IKK activation