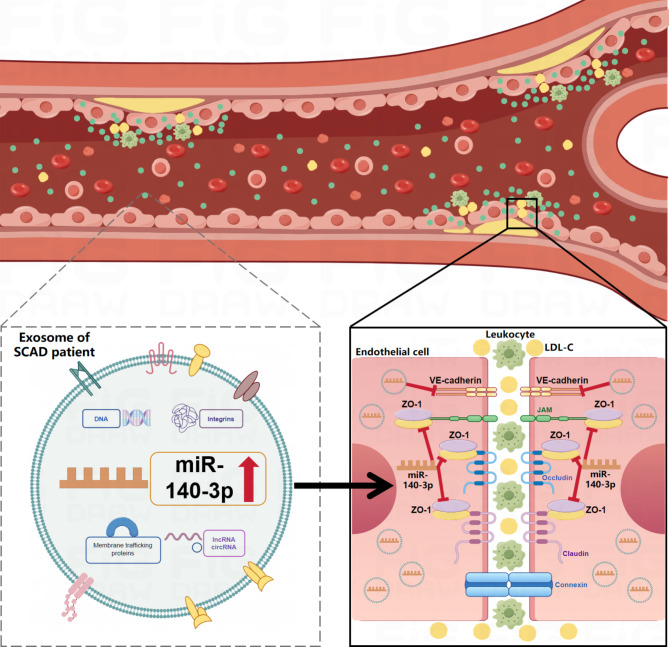
Fig. 7.
Hypothesis model for the role of ExoSCAD in atherosclerosis. ExoSCAD suppress VE-Cad and ZO-1 expressions in endothelial cells to impair vascular endothelial junctions, leading to lipids and leukocytes to cross the endothelial barrier and deposit in the subendothelial layer, thereby deteriorating atherosclerosis. Notably, overexpressed miR-140-3p is transferred from ExoSCAD into endothelial cells to inhibit ZO-1. ExoSCAD: plasma exosomes of patients with stable coronary artery disease; LDL-C: low density lipoprotein cholesterol.