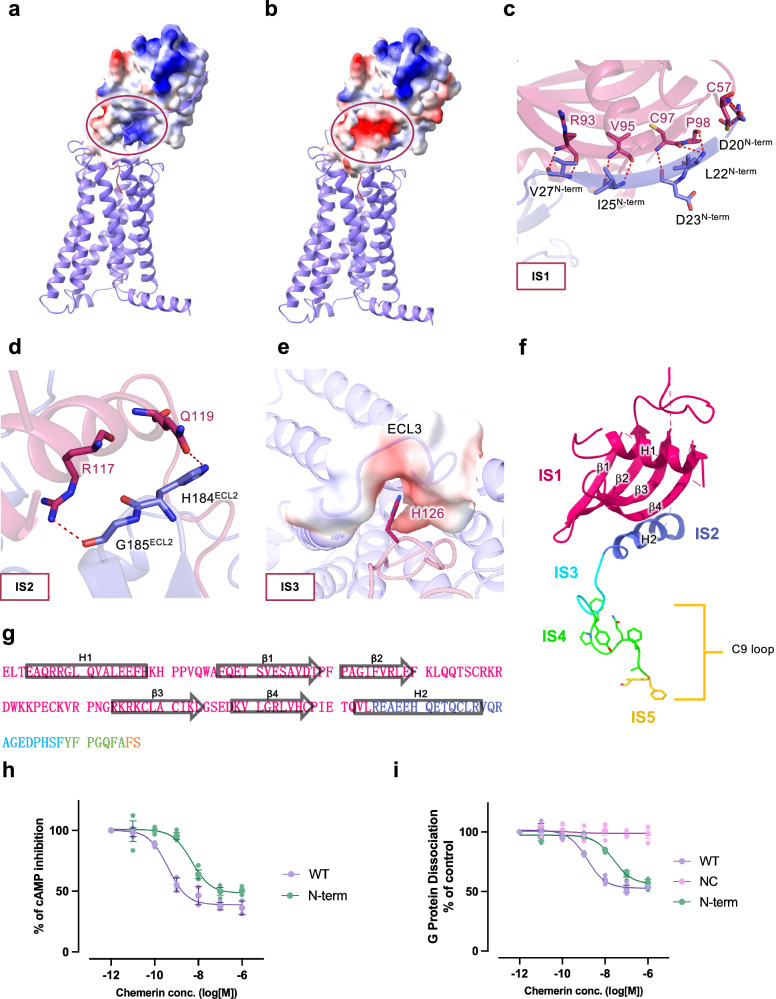
Fig. 2. Molecular interactions between the main body of chemerin and CMKLR1.
Chemerin is shown in magenta and CMKLR1 is shown in purple. a, b Electrostatic potential surface of (a) chemerin and (b) the N-terminus of CMKLR1. The circles mark the site where the N-terminal β-strand of CMKLR1 interacts with the β4-strand of chemerin (IS1). c Polar interactions at IS1. Hydrogen bonds between residues of chemerin and the N-terminal β-strand of CMKLR1 are shown in red dashes. d Polar interactions at IS2 of chemerin (magenta) with ECL2 of CMKLR1 (purple). Hydrogen bonds are shown in red dashes. e Electrostatic interactions at IS3 of chemerin with ECL3 of CMKLR1. The electrostatic potential surface of ECL3 and H126 of chemerin are shown. f, g Illustrations of chemerin interaction sites (f), and amino acid sequence of chemerin with IS1-5 highlighted in different colours (g). h cAMP inhibition assay in cells expressing wild-type and N-terminus truncated CMKLR1. i G protein dissociation assay in cells expressing wild-type and N-terminus truncated CMKLR1. Data are shown as mean ± SEM from n = 3 independent experiments.