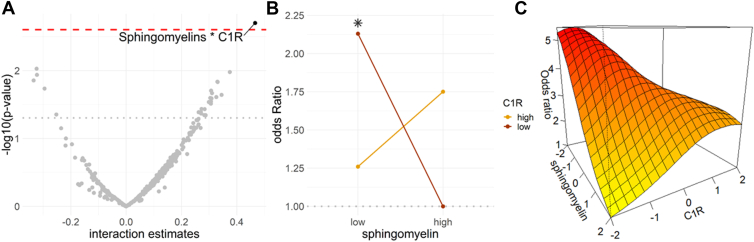
Figure 13.
A, Interaction estimates corresponding to all the combinations between the complement proteins (n = 16) and lipids (n = 23) selected by multiblock sPLS-DA model (at a cutoff 0.50), i.e., the interaction candidates. Estimates above the dotted red line corresponded to the significant interactions after correction for multiple testing. B and C increased in the odds of AMD (expressed in odds ratio) according to sphingomyelin and C1R using a logistic regression adjusted on age, sex, hypertension, diabetes, body mass index, smoking status, and lipid-lowering medications (with sphingomyelin and C1R considered as binary variables with low and high values corresponding to values lower and higher than the median) (B); and using a generalized additive model adjusted on the same variables (with sphingomyelin and C1R considered as continuous variables) (C). The asterisk in panel B corresponds to a significant effect. AMD = age-related macular degeneration; C1R = complement protein 1R; sPLS-DA = sparse projection to latent structure-discriminant analysis.