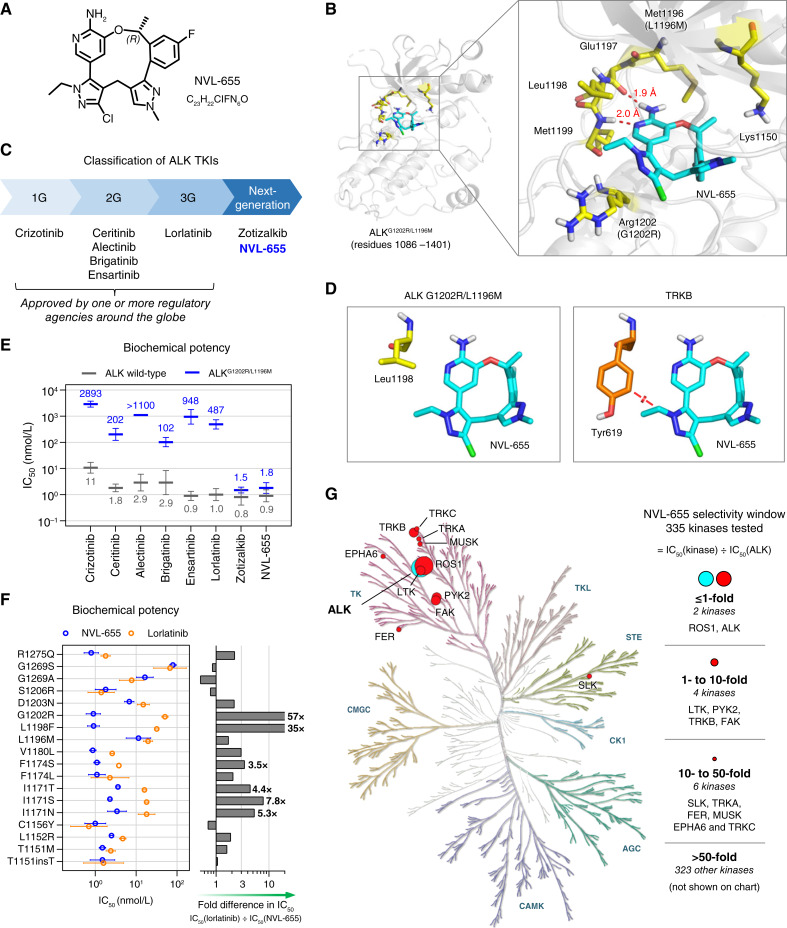
Figure 1.
Design and biochemical activity of NVL-655. A, Chemical structure of NVL-655. B, X-ray structure of NVL-655 (cyan) in the binding pocket of ALKG1202R/L1196M, with key residues highlighted in yellow and hydrogen bonds in red. C, Classification of ALK TKIs into 1G, 2G, 3G, or next generation. D, Positioning of NVL-655 with respect to Leu1198 in the crystal structure of ALKG1202R/L1196M (left, yellow; PDB: 9GBE) or Tyr619 in TRKB (right, orange; PDB: 4AT3) based on α-carbon superposition. Red disc indicates a steric clash based on van der Waals overlap. E, Activity of eight TKIs against ALK (gray) and ALKG1202R/L1196M (blue) in biochemical assays. Geometric mean and SD are plotted, with numerical values of the means shown. “IC50 >” is treated as “IC50 =” for plotting. F, Biochemical activity of NVL-655 (blue) and lorlatinib (orange) against ALK with single amino acid substitution or insertion. Geometric mean and SD are plotted. Graph indicates relative potency to NVL-655. G, Kinome selectivity tree for NVL-655. Twelve kinases inhibited with IC50 within 50-fold of ALK are indicated.