Fig. 2.
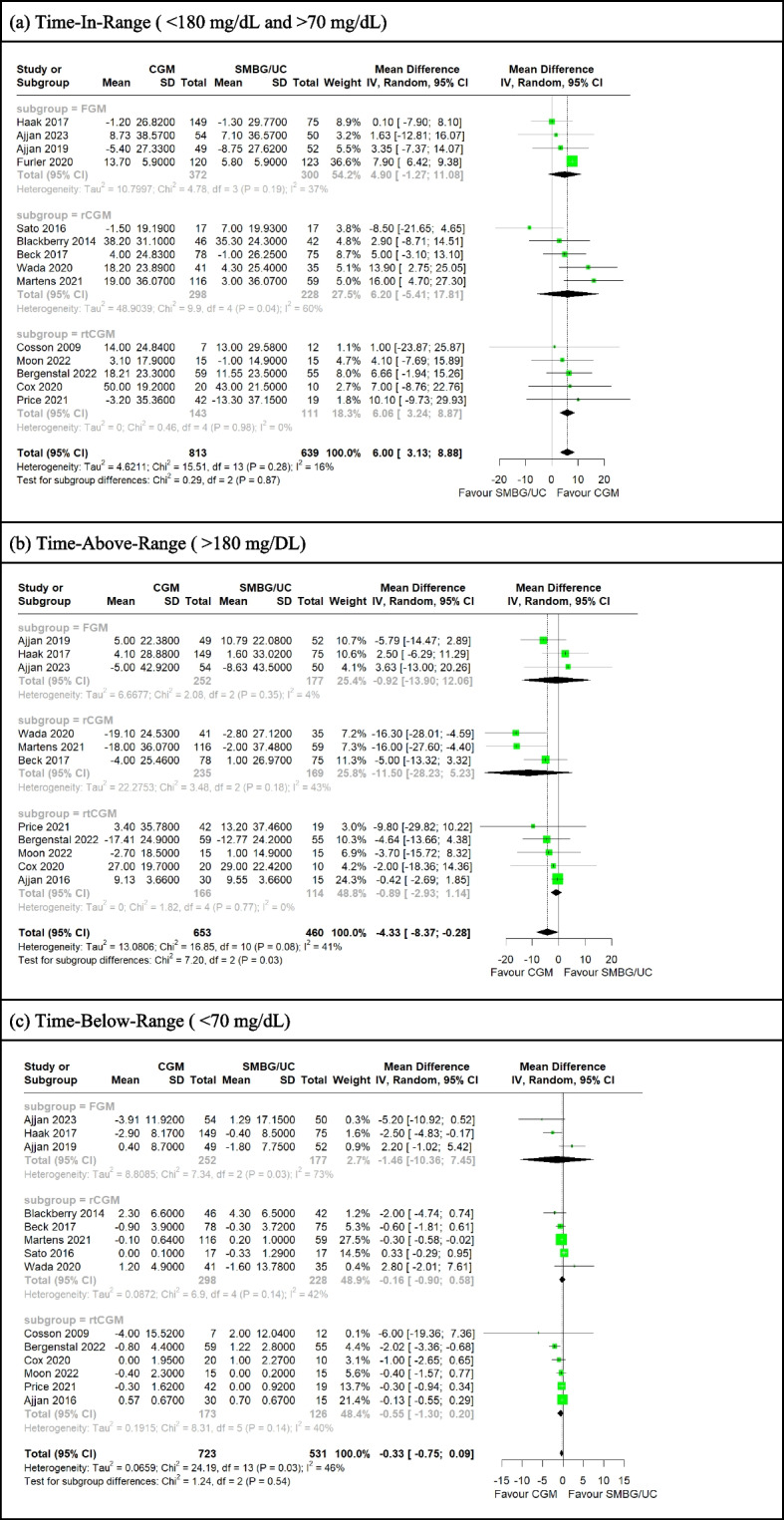
a-c Forest plot for meta-analysis of primary studies comparing CGM with SMBG from 2009 to 2023 by pooling the mean difference in pre-post change of (a) TIR, (b) TAR and (c) TBR between CGM and SMBG/UC participants. CGM significantly associated with greater TIR increase (MD= 6.00 [95%CI: 3.13 to 8.88]) and greater TAR decrease (MD= −4.33 [95%CI: −8.37 to −0.28]), and insignificantly associated with greater TBR decrease (MD= −0.33 [95%CI: −0.75 to 0.09]) over SMBG/UC participants. TIR and TBR were invariant with CGM modality (p = 0.87, p = 0.54) but not TAR (p = 0.03)
