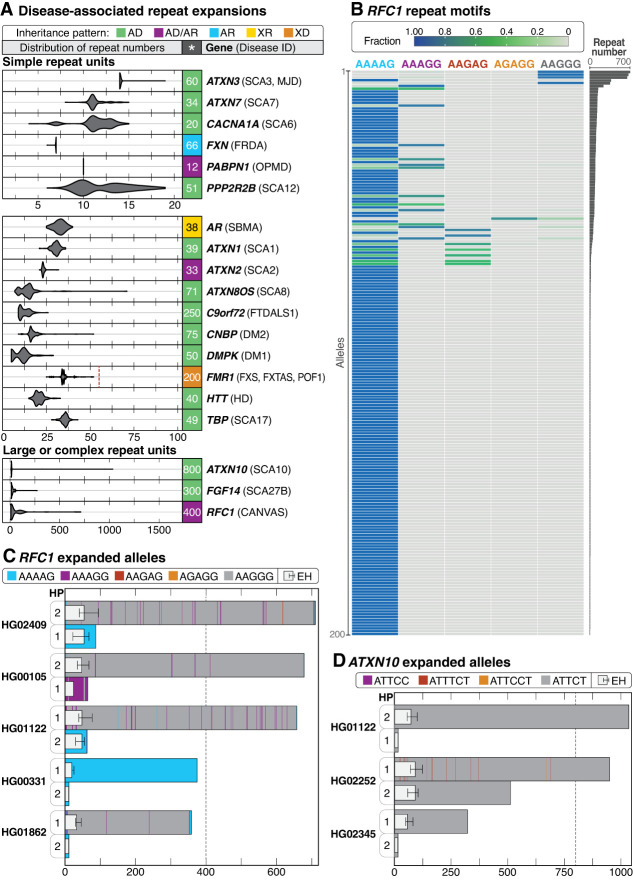
Figure 4.
Evaluation of repeat expansions known to be associated with Mendelian conditions. (A) Haplotype-resolved repeat expansions of selected repeat loci for simple and complex repeat units. Pathogenic repeat size is shown to the right of each plot (*), the associated condition is in parentheses, and the full name of each condition can be found in Supplemental Table S11. The pathogenic repeat size for FMR1 is listed as 200 repeats, but a dashed vertical line represents the 55-repeat threshold that puts 46,XX and 46,XY individuals at risk for fragile X-associated tremor/ataxia syndrome (FXTAS, MIM #300623) and 46,XX individuals at risk of fragile X-associated primary ovarian insufficiency (POF1/FXPOI, MIM #311360). (AD) autosomal dominant, (AD/AR) autosomal dominant/recessive, (AR) autosomal recessive, (XR) X-linked recessive, (XD) X-linked dominant. (B) Among 200 haplotypes (y-axis), an expansion in RFC1 near or over 400 repeat units was seen in five haplotypes. AAGGG is the most common pathogenic repeat expansion; additional pathogenic expansions include ACAGG (not shown), and a mixed AAAGG/AAGGG expansion (Cortese et al. 1993). (C) Haplotype (HP)-resolved detail of RFC1 repeat expansions in five samples with an expansion of one allele. Haplotypes are assigned arbitrarily. The dotted line represents the position of full penetrance alleles typically seen at 400 repeat units. (D) Three samples with expansions in ATXN10 larger than 280 ATTCT repeats were observed. The dotted line at 800 repeat units represents the position of the lower end of the full penetrance range. ExpansionHunter (EH) estimates are overlayed atop the bar plots in (C) and (D), placed on HP1 or HP2 based on their length.