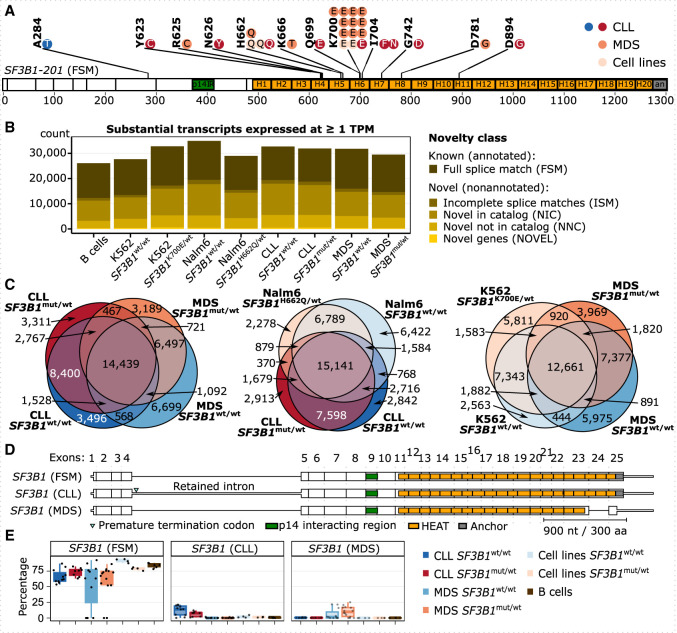
Figure 1.
Long-read sequencing of CLL and MDS patient samples discovers novel isoforms. (A) Distribution of SF3B1 mutations in CLL and MDS patient samples used for Iso-Seq; each dot represents a mutated sample. One CLL patient is marked twice owing to two mutations (I704N and D894G). Note that the A284T mutation is outside the HEAT repeat domains and thus was grouped as a wild-type sample, also according to further analysis described below. SF3B1 is shown as the major isoform expressed, with the full splice match (FSM) to annotated isoform 201. (B) The number of substantial transcripts identified in each group and expressed at the level of at least one transcript per million (TPM) colored by the category of isoform novelty: with FSM, with incomplete splice matches (ISMs), with combinations of annotated splice junctions (novel in catalog [NIC]), with at least one novel splice site (novel not in catalog [NNC]), or from novel genes (NOVEL) (Tardaguila et al. 2018). (C) Venn diagrams showing the overlap between isoforms from B expressed at one or more TPM in each group. (D) SF3B1 isoforms expressed at >10% relative expression level. (E) Relative expression levels of SF3B1 isoforms from D.