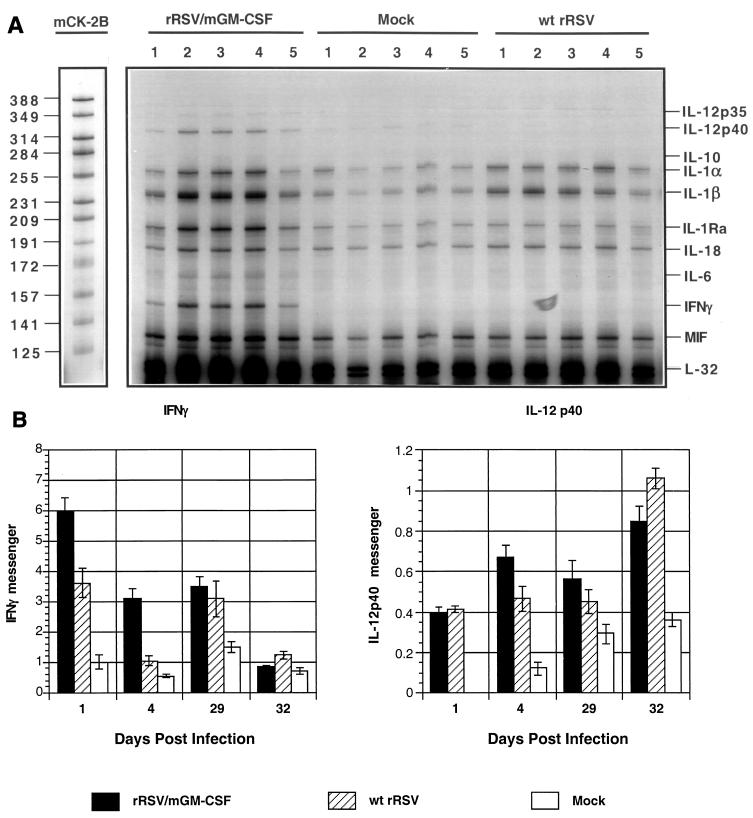
FIG. 5.
Detection of pulmonary cytokine and chemokine mRNAs by an RNase protection assay. Animals (20 per group) were mock infected or infected with 106 PFU of rRSV/mGM-CSF or wt rRSV per animal on day 0. Five mice per group per time point were sacrificed on days 1 and 4, and total pulmonary RNA was isolated and analyzed by an RNase protection using mixed probes specific to selected cytokines and chemokines. The remaining animals were challenged by infection with 106 PFU of wt RSV on day 28; five mice per group per time point were sacrificed on days 29 and 32, and total pulmonary RNA was isolated and analyzed in the same way. (A) Autoradiogram showing the results for one probe kit, mCK-2B, for mRNA isolated on day 4, with each gel lane representing an individual mouse and unhybridized probe mix run in parallel as a marker, with the nucleotide lengths of individual probes shown on the left. Protected probes corresponding to individual cytokines or the housekeeping gene L-32 are identified on the right. IL-1Ra, IL-1 receptor antagonist; MIF, macrophage migration inhibitory factor; IL-12 p35 and p40, constitutive and inducible monomers of IL-12, respectively. (B) Accumulation of pulmonary mRNA for IFN-γ and the inducible p40 monomer of dimeric IL-12. Autoradiograms such as those shown in panel A were quantified by phosphorimagery and calculated as a percentage of the amount of L-32 housekeeping gene mRNA in the same sample. Mean values of five mice per virus per day (with SE) are shown. Note that each y axis has a different scale.